| Cardiology Research, ISSN 1923-2829 print, 1923-2837 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Cardiol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.cardiologyres.org |
Original Article
Volume 10, Number 5, October 2019, pages 303-308
Efficacy and Safety of Subcutaneous Fellow’s Stitch Using “Fisherman’s Knot” Technique to Achieve Large Caliber (> 10 French) Venous Hemostasis
Prakash Kumara, Puneet Aggarwaalb, Santosh Kumar Sinhab, c, Umeshwar Pandeyb, Mahmodula Razib, Awdesh Kumar Sharmab, Ramesh Thakurb, Chandra Mohan Varmab, Vinay Krishnab
aDepartment of Cardiology, Rajendra Institute of Medical Science, Ranchi, Jharkhand, India
bDepartment of Cardiology, LPS Institute of Cardiology, G.S.V.M. Medical College, Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh 208002, India
cCorresponding Author: Santosh Kumar Sinha, Department of Cardiology, LPS Institute of Cardiology, G.S.V.M. Medical College, Kanpur, Uttar Pradesh 208002, India
Manuscript submitted August 14, 2019, accepted August 31, 2019
Short title: Fellow’s Stitch Using “Fisherman’s Knot”
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/cr931
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Background: Among patients undergoing intervention involving venous access, various techniques have been implemented to achieve hemostasis in order to reduce local access site complications, to decrease length of stay and to facilitate early ambulation. We aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of fellow’s stitch using “fisherman’s knot” (figure of Z (FoZ)) technique when compared with conventional manual compression for immediate closure of large venous sheath (> 10 French (Fr)).
Methods: Between November 2012 and March 2019, 949 patients underwent various interventions which involved venous access requiring hemostasis. All the patients were anticoagulated with heparin during the procedure. In a sequential allocation, fellow’s stitch using “fisherman’s knot” (group I: n = 384) and conventional manual compression (group II: n = 365) were used in achieving hemostasis at right/left femoral venous access site following sheath removal (> 12 Fr). A 0-Vicryl suture was used to make one deep stitch just distal to entry of sheath and one superficial stitch just proximal to entry site, thereby creating an FoZ. A fisherman’s knot was then tied, and knot was pushed down while sheath was removed. In cases where immediate hemostasis was not achieved, it was compressed for 2 min to achieve it.
Results: The mean age of 949 patients was 13.1 ± 8.2 years where male (n = 574; 65%) outnumbered female (n = 375; 35%). In group I, hemostasis was achieved immediately after tying the knot in 343 (89.3%) patients, while within ≤ 2 min of light pressure in 41 (10.7%) patients. Five (1.3%) patients had failure of stitch as suture snapped during knotting, and hemostasis was achieved by manual compression as per protocol in group I. The median time to hemostasis (1.1 vs. 14.3 min, P < 0.001), ambulation (3.3 vs. 18.9 h, P < 0.01) and hospital stay (24.6 vs. 36.8 h, P < 0.001) was significantly shorter in group I compared to group II. The minor vascular access site complications in form of hematoma (n = 6 (1.6%) vs. n = 1 (0.2%); P < 0.001), and thrombosis at femoral vein (n = 4 (1.1%) vs. n = 0 (0%); P < 0.001) were significantly higher in group II when compared to group I. The differences regarding re-bleeding and formation of arterio-venous fistula between both the groups were statistically insignificant.
Conclusion: The fellow’s stitch using “fisherman’s knot” or “FoZ” suture is a simple, efficacious and safe technique to achieve an immediate hemostasis after removal of larger venous sheath (> 10 Fr).
Keywords: Fellow’s stitch; Fisherman’s knot; Figure of Z; Venous hemostasis
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Venous access site complications are one of the most common complications among interventions like device closure of atrial septal defect (ASD), patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), ruptured sinus of Valsalva aneurysm (RSOVA), balloon pulmonary valvuloplasty (BPV), percutaneous transmitral commissurotomy (PTMC), cryoablation for arrhythmias and percutaneous mitral valve repair (mitra clip). These procedures require large sheath placement (10 - 14 French (Fr)) and many of these patients have already received vitamin K antagonist which further enhance the complication rates such as groin hematoma, retroperitoneal bleeding, femoral pseudoaneurysm, or femoral arteriovenous fistula. These are associated with increased morbidity and mortality, prolonged hospital stay, and sometimes require surgical exploration as well [1-4]. Conventionally manual compression with pressure dressing was the most commonly used technique in the past, but recently it has been dealt with device-based suture closure (perclose device, angio-seal). Newer techniques are associated with risk of device failure and vascular complications, and increase the cost which is a big challange especially in developing countries like India where not many patients are ensured. Recently, fellow’s stitch using “fisherman’s knot” (figure of Z (FoZ)) technique to achieve femoral venous hemostasis after removal of large-caliber venous sheaths has been introduced [5, 6]. Here, its immediate and short-term (3 months) efficacy and safety was assessed with conventional manual compression among mixed population (mainly pediatric) of patients.
| Materials and Methods | ▴Top |
Design
To assess efficacy and safety of fellow’s stitch using “fisherman’s knot” technique to achieve large caliber (> 10 Fr) venous hemostasis. This was a prospective, randomized, single-center study conducted in the Department of Cardiology, LPS Institute of Cardiology, G.S.V.M. Medical College, Kanpur, UP, India from January 2013 to March 2019. A total of 949 consecutive patients were enrolled who underwent ASD device closure, PDA device closure, RSOV device closure, BPV and PTMC. The study protocol was approved by the local ethics committee and followed the Declaration of Helsinki after obtaining informed consent from each patient.
Procedure
Enrolled patients underwent comprehensive evaluation including detailed clinical examination and investigations including electrocardiogram, cardiac catheterization and 2D echocardiogram (VIVID7; GE Healthcare, Germany). After completion of the procedure, venous sheath was removed and hemostasis was achieved using either fellow’s stitch or manual compression. All patients were anticoagulated with unfractionated heparin at dosage of 80 - 100 U/kg during the procedure.
Post-procedural sheath removal
In fellow’s stitch group, venous sheath (right or left) was removed just after the procedure while patient was still on operation table. On the contrary, in manual compression group, venous sheath was removed after patient was shifted out of catheterization lab in the recovery area. Both were performed without activated clotting time (ACT) measurement. Arterial hemostasis (in cases of PTMC and RSOVA closure) was achieved by manual compression after completion of the procedure.
The fellow’s stitch (fisherman’s knot)
A 0-Vicryl suture on a large-curved cutting needle was passed little distal (5 - 10 mm) to entry point of sheath into skin below the sheath and advanced through the subcutaneous tissue holding its generous amount but without going too deep to ligate the femoral vein (Figs. 1, 2a). The needle and suture were crossed over the sheath (Fig. 2b). Similarly, a second pass of the needle was obtained little proximal (5 - 10 mm) to entry point of sheath into skin but advancing above the sheath through the subcutaneous tissue (Fig. 3a). Therefore, the entry, exit and course of suture imparted an FoZ (Fig. 3a). As sheath was pulled out, suture was tightened so that subcutaneous tissue was bunched up for hemostasis (Fig. 3b). Both the free ends were then tied using fisherman’s knot over the entry point of sheath giving it appearance of figure-of-eight (FoE). After first knot, sheath was pulled out gently and removed (Fig. 4a). Following removal of sheath, few more (3 - 4) reinforcement knots were tied, thus tightening the suture so that subcutaneous tissue was folded up to achieve immediate hemostasis (Fig. 4b). The detail method has been illustrated in Figure 5. In cases where immediate hemostasis was not achieved because of slight bleeding (oozing), gentle pressure was applied for 2 min over the knot. Once the bleeding stopped, it was covered by sterile gauze. The patient was shifted and closely monitored in the intensive care unit. Compression bandages were not used in the suture group. The sutures were removed after 4 - 6 h.
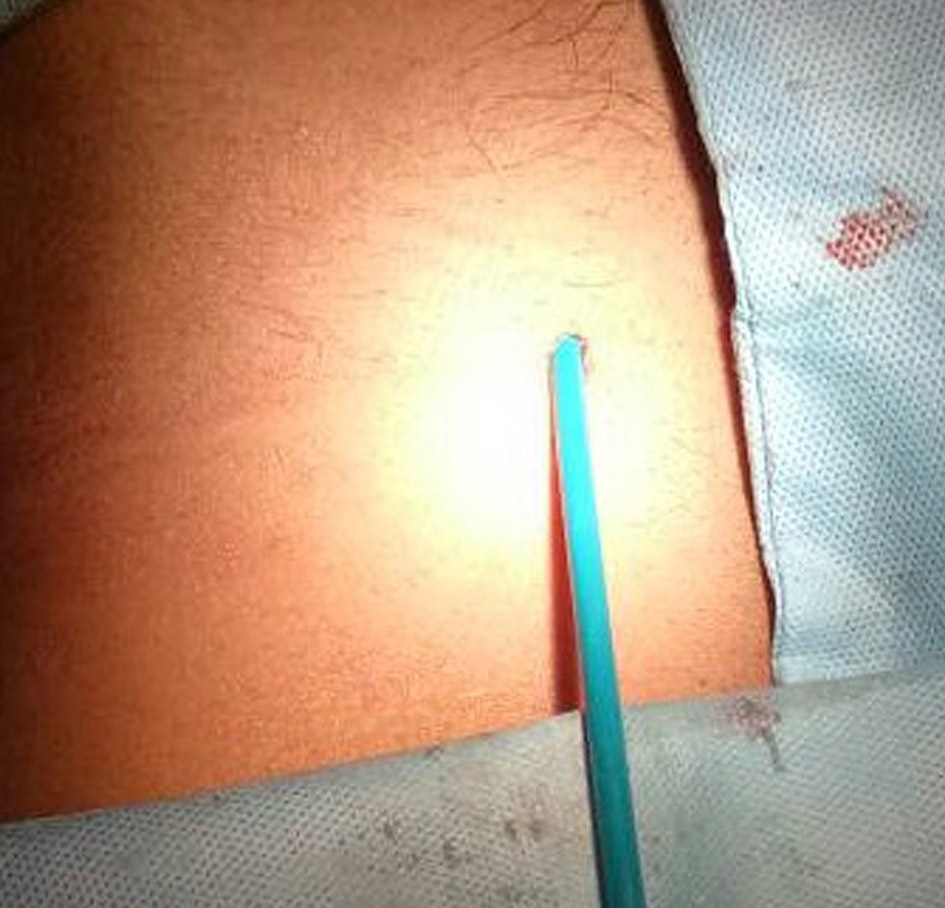 Click for large image | Figure 1. Point of entry of sheath into skin. |
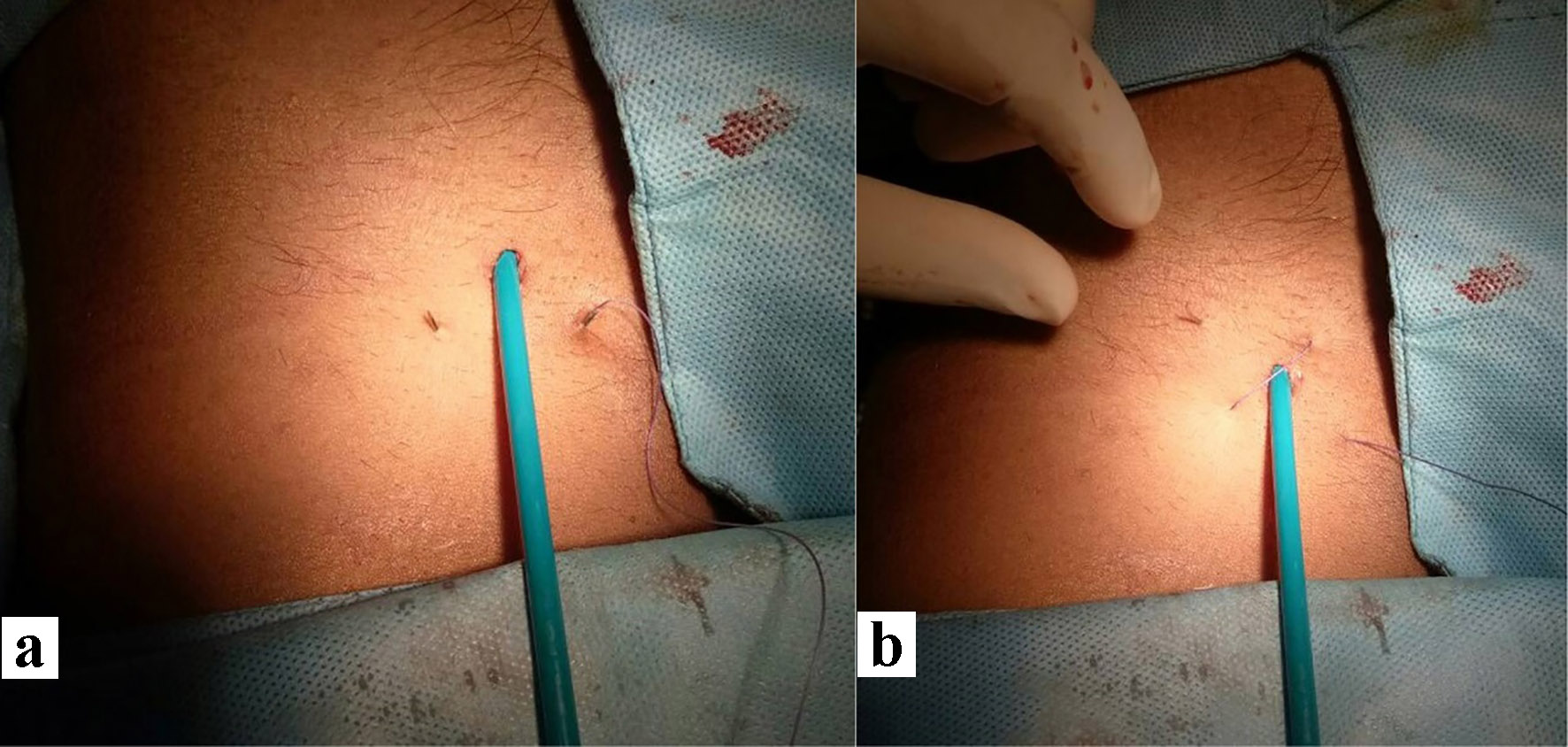 Click for large image | Figure 2. First pass of suture by crossing below the sheath and skin caudal to entry point (a). The needle and suture were crossed over the sheath and making second pass (b). |
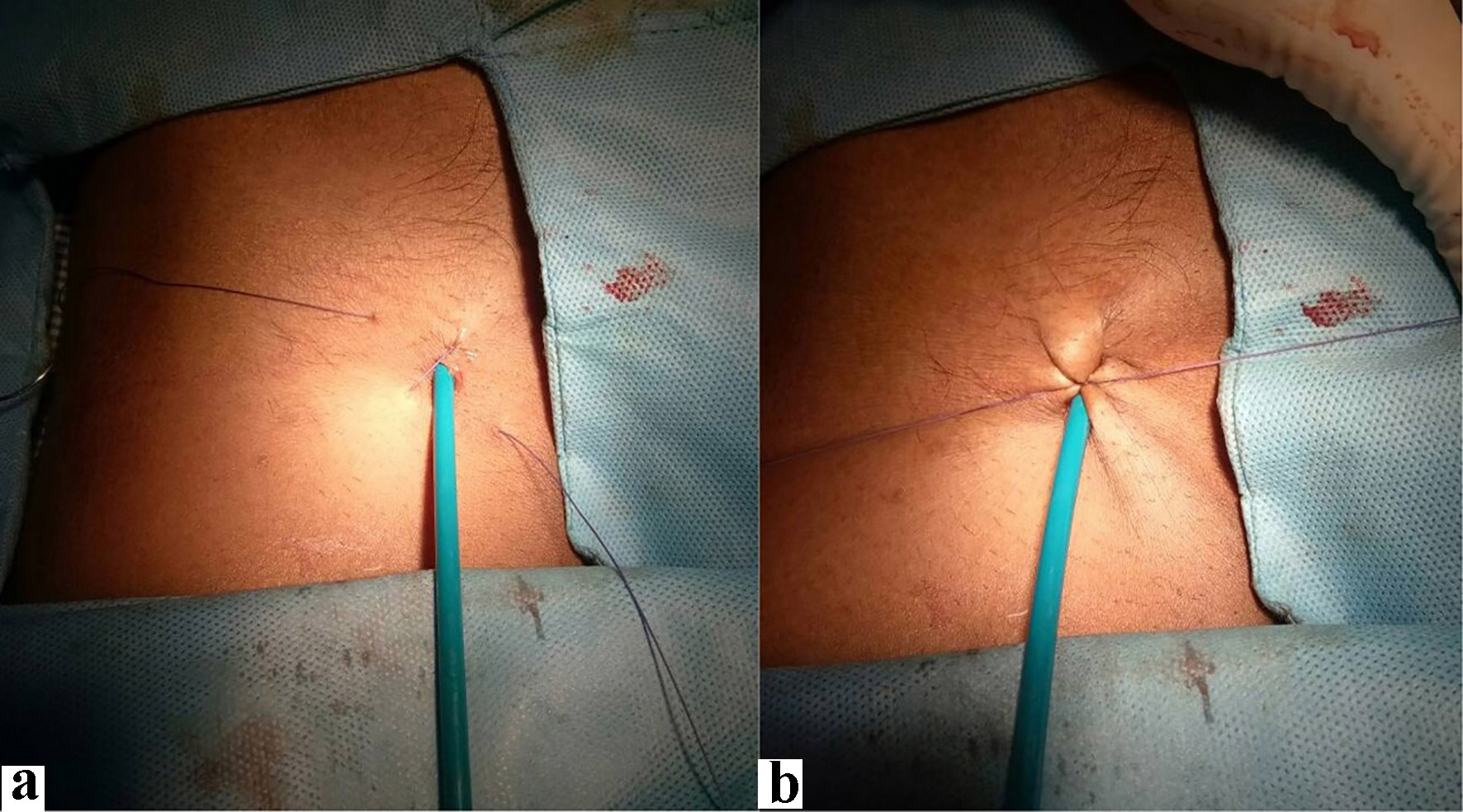 Click for large image | Figure 3. The entry, exit and course of suture imparted a figure of Z (a). Both the free ends were then tied using fisherman’s knot over the entry point of sheath giving it appearance of figure-of-eight (FoE; b). |
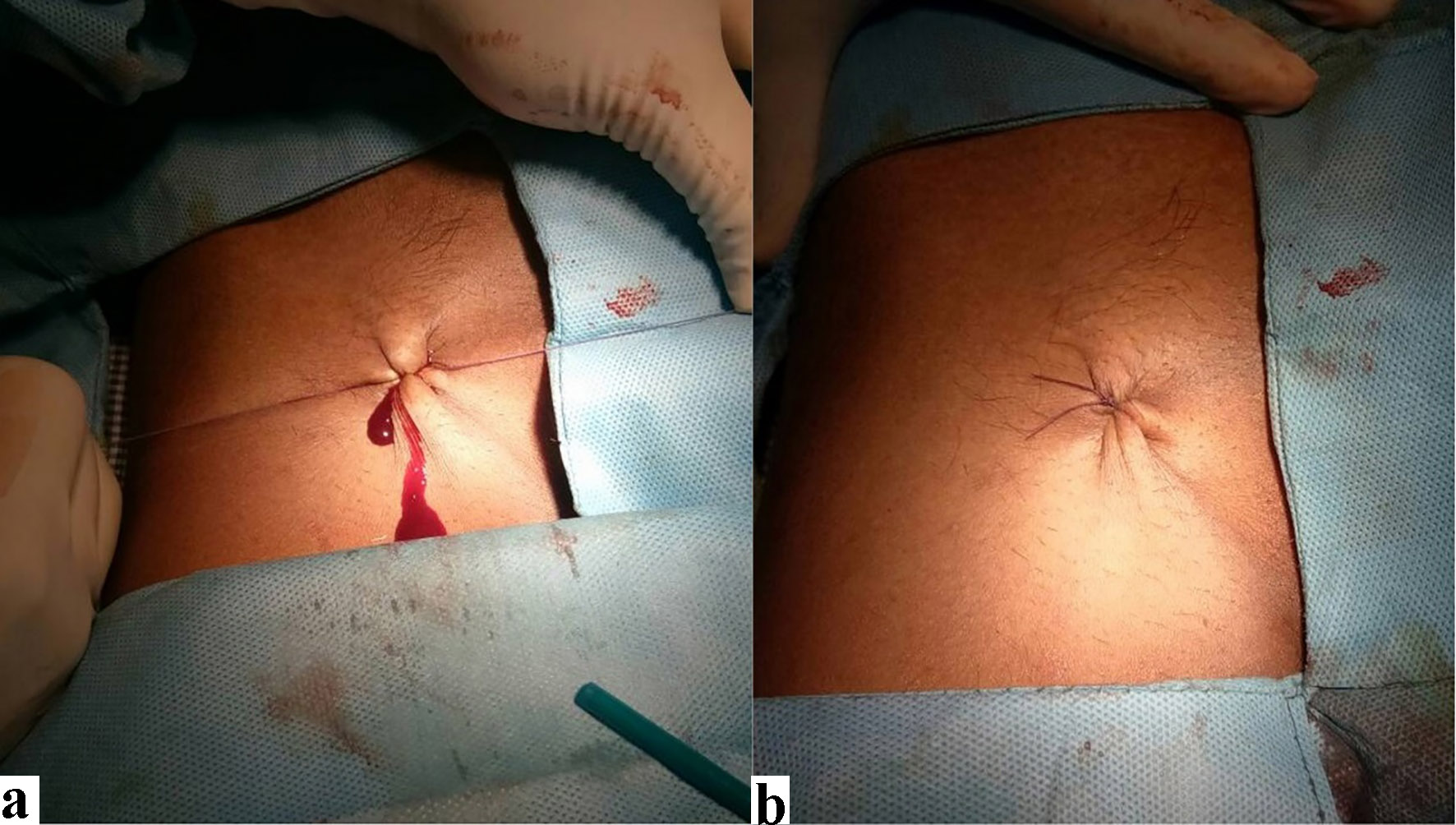 Click for large image | Figure 4. After first knot, sheath was pulled out gently and removed (a). Following removal of sheath, few more (3 - 4) reinforcement knots were tied, thus tightening the suture so that subcutaneous tissue was folded up achieving immediate hemostasis (b). |
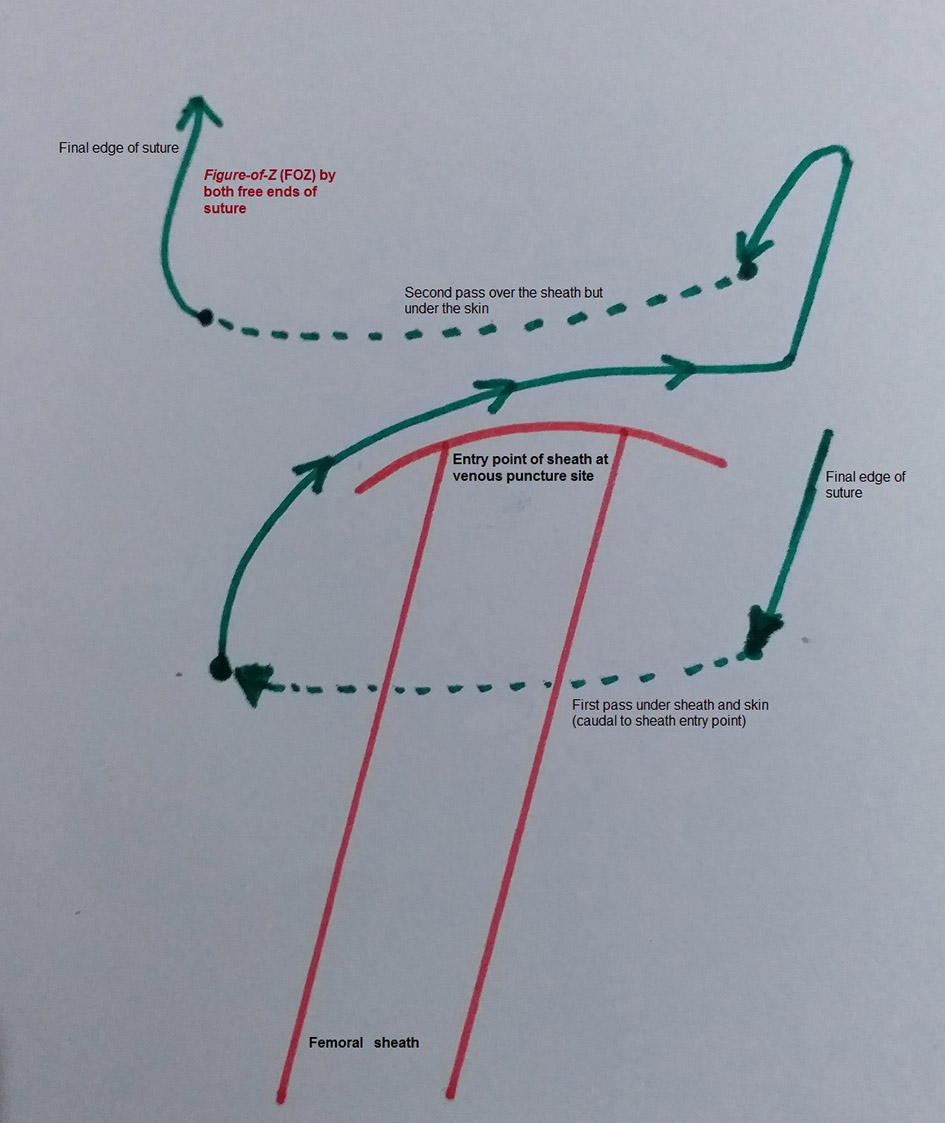 Click for large image | Figure 5. The basic steps of the fellow’s stitch using fisherman’s knot. |
The sheath size (in French) plus one minute was taken as minimum compression time in manual compression group (group II). If adequate hemostasis was achieved, compression dressing using dynaplast (an elasticized bandage) was then applied for 1 - 2 h. In cases where it was inadequate, compression was prolonged. Following this, all patients were observed for the occurrence of hematoma, fistula formation, or thrombotic complications. In cases where these were needed to be evaluated, common femoral vein (CFV) was probed using 10 MHz linear transducer (VIVID7; GE Healthcare).
Statistical analyses
Statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS 19.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL). All continuous data were reported as mean ± standard deviation, and all categorical data were reported as frequencies and/or percentages. The comparison between groups was done by Mann-Whitney U test for continuous variables and by Chi-square or Fisher’s exact test for categorical variables. P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
| Results | ▴Top |
The mean age of 949 patients who were enrolled was 13.1 ± 8.2 years where male (n = 574; 65%) outnumbered female (n = 375; 35%). Baseline clinical and procedural characteristics were equally matched for both groups as shown in Table 1. PTMC was done in 475 (63.4%) patients because of rheumatic mitral stenosis whereas ASD device closure was performed in 198 (26.5%) patients. BPV and device closure of PDA and RSOV were the rest. Sixty-eight (9.1%) patients received warfarin (oral vitamin K antagonist) for various atrial arrhythmias where majority were suffering from rheumatic mitral stenosis. 12 F was the most common sheath size (n = 537;71.6%) as a result of PTMC which was performed in 475 (63.4%) and ASD device closure in 62 (8.2%) patients. All 14-Fr sheaths were used in patients in whom ASD device closure was performed (Table 1).
 Click to view | Table 1. Baseline Characteristics of Patients (n = 749) |
Acute procedural success was achieved in all patients. Procedural time and heparin doses during procedure were also similar in between fellow’s stitch and manual compression groups. In the fellow’s stitch group, venous hemostasis was achieved immediately after tying the knot (n = 343; 89.3%) or within ≤ 2 min of light pressure (n = 33; 8.6%). Stitch failure was noted in five (1.3%) patients as a result of snapping of suture during knotting where hemostasis was achieved by manual compression as per protocol. The median time to hemostasis (1.1 vs. 14.3 min; P = 0.004), time spent in recovery room (2.1 vs. 21.6 min; P = 0.003), ambulation time (3.3 vs. 18.9 h; P = 0.005), hospital stay (24.6 vs. 36.8 h; P = 0.005), hematoma (0.2% vs. 1.6%; P = 0.005) and thrombosis of femoral vein (0% vs. 1.1%; P = 0.005) were significantly shorter in fellow’s stitch group than manual compression group whereas cross-over as a result of stitch failure (1.3% vs. 0%; P = 0.002) was higher in fellow’s stitch group (Table 2). There was no significant difference in arterio-venous fistula formation, and re-bleeding between both groups (Table 2).
 Click to view | Table 2. Procedural Outcome of Patients (n = 749) |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
With the increasing use of anticoagulation and antiplatelet agents during various cardiac catheterization procedures, the rate of local access site complications has increased. Manual compression has been the gold standard to achieve hemostasis. Gradually, it saw transition from collagen-based devices to device-based suture closure, finally culminating to subcutaneous suture closure which facilitated early ambulation and discharge with fewer complications.
A subcutaneous fellow’s stitch using fisherman’s knot appears a safe and efficacious method in achieving venous hemostasis using larger sheath (≥ 10 F). The deployment technique is quite easy to learn and can be performed in < 20 s. As it allows hemostasis to be achieved rapidly, it significantly cuts down the turnover time. The overall success rate in our study was 98.7% which is similar to the study reported by Shaw et al [7]. The cross-over rate in our study was 1.3% (five cases in 384) which was seen among the earlier recruiters in initial part of study. It was ascribed to suture breaking, and knot slippage as a result from poor knot tying technique. Three out of five cases (60%) were the overweight female who had undergone ASD closure whose thigh was bulky which resulted in knot slippage. After passing through initial learning curve which is inherent to any new procedure, the failure rate came down.
This technique, also known as “FoE” or “FoZ”, was first reported by Bagai and Zhao [8] who employed this suture technique to achieve femoral venous hemostasis in the adult. The external soft tissue compression at entry point of sheath leads to occlusion by means of vasoconstriction of common femoral vein, achieving venous hemostasis as demonstrated by Mehmet et al [9]. It is temporary as there is no thrombosis, embolism, or venous stenosis as seen by vascular ultrasound after suture removal. As time to hemostasis is very short, time spent in recovery room, ambulation time and overall hospital stay are significantly less in fellow’s stitch group.
In our study, 26% (99) of patients were children (< 12 years), which tells that this technique is safe and feasible among pediatric population as well which is quite similar to study reported by Zhou et al [10] among larger population group (102 patients). In their study, two patients (01.8%) had reported local site hematomas while none were reported in < 12 years age group. Local hematoma was reported in one adult patient (0.9%) who underwent mitral valvulotomy in lieu of mitral stenosis and was receiving warfarin because of atrial fibrillation. As his built was thin, suture depth remained shallow resulting in hematoma. It was aborted with manual compression. Re-bleeding was reported in all those patients who had stitch failure and hemostasis was achieved by manual compression.
The economical impact of this technique is huge especially in developing countries like India where mechanized suture delivery device, like PerClose™ (Abbott vascular, USA), angio-seal (St. Jude, USA), Star Close vascular closure system and Vasoseal are not covered by medical insurance. Average cost saving is around $175 - $200. Furthermore, only single fellow’s stitch is sufficient across all sheath size where mechanized suture delivery devices have gotten limitation as one can be employed for 12 Fr sheath, and an additional one will be required to secure the hemostasis for > 12 Fr sheath which will further increase procedural time and make it costlier.
Arteriovenous fistula is the result of femoral puncture per se and not a complication of the suture technique. There were none in either group in our study. Though this technique utilizes suture, it remains outside the vessel while in other vascular closure devices, some part stays intravascular. In our study, no local site infection was noted while one patient developed a Staphylococcus infection at the groin site requiring prolonged hospitalization as reported by Shaw et al [7]. Another developed deep venous thrombi and pulmonary emboli. In both cases, there were both arterial and venous access sites [7].
Conclusion
Subcutaneous temporary “fellow’s stitch” is a simple, clinically cost effective, efficacious and safe technique to achieve immediate post-procedure venous hemostasis for sheath sizes at least up to 14 Fr among wide variety of population group.
Acknowledgments
Thanks are given to R. N. Pandey for technical support in performing device closure of ASD.
Financial Disclosure
None to declare.
Conflict of Interest
None to declare.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained.
Author Contributions
Substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; or the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data for the work: PK, PA, SKS, UP, MR, AKS, RT, CMV, VK. Drafting the work or revising it critically for important intellectual content: PK, PA, SKS, UP, MR, AKS, RT, CMV, VK. Agreement to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved: PK, PA, UP, RT, CMV, VK. Final approval of the version to be published: SKS, UP, MR, AKS, RT, CMV, VK.
| References | ▴Top |
- Geis NA, Pleger ST, Chorianopoulos E, Muller OJ, Katus HA, Bekeredjian R. Feasibility and clinical benefit of a suture-mediated closure device for femoral vein access after percutaneous edge-to-edge mitral valve repair. EuroIntervention. 2015;10(11):1346-1353.
doi pubmed - Maraj I, Budzikowski AS, Ali W, Mitre CA, Kassotis J. Use of vascular closure device is safe and effective in electrophysiological procedures. J Interv Card Electrophysiol. 2015;43(2):193-195.
doi pubmed - Mahadevan VS, Jimeno S, Benson LN, McLaughlin PR, Horlick EM. Pre-closure of femoral venous access sites used for large-sized sheath insertion with the Perclose device in adults undergoing cardiac intervention. Heart. 2008;94(5):571-572.
doi pubmed - Wiley JM, White CJ, Uretsky BF. Noncoronary complications of coronary intervention. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2002;57(2):257-265.
doi pubmed - Cilingiroglu M, Salinger M, Zhao D, Feldman T. Technique of temporary subcutaneous "Figure-of-Eight" sutures to achieve hemostasis after removal of large-caliber femoral venous sheaths. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;78(1):155-160.
doi pubmed - Morgan GJ, Waragai T, Eastaugh L, Chaturvedi RC, Lee KJ, Benson L. The fellows stitch: large caliber venous hemostasis in pediatric practice. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2012;80(1):79-82.
doi pubmed - Shaw JA, Dewire E, Nugent A, Eisenhauer AC. Use of suture-mediated vascular closure devices for the management of femoral vein access after transcatheter procedures. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2004;63(4):439-443.
doi pubmed - Bagai J, Zhao D. Subcutaneous "figure-of-eight" stitch to achieve hemostasis after removal of large caliber femoral venous sheaths. Cardiac Interv Today. 2008;4:22-23.
- Mehmet C, Michael S, Zhao D, Feldman T. Technique of temporary subcutaneous "figure-of-eight" sutures to achieve hemostasis after removal of large caliber femoral venous sheaths. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2011;78:155-160.
doi pubmed - Zhou Y, Guo Z, Bai Y, Zhao X, Qin Y, Chen S, Wu H, et al. Femoral venous hemostasis in children using the technique of "figure-of-eight" sutures. Congenit Heart Dis. 2014;9(2):122-125.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cardiology Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.


