| Cardiology Research, ISSN 1923-2829 print, 1923-2837 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Cardiol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website http://www.cardiologyres.org |
Case Report
Volume 10, Number 4, August 2019, pages 249-252
Spontaneous Hemorrhagic Pericardial and Pleural Effusion in a Patient Receiving Apixaban
Michael Cinellia, c, Asif Uddina, Ilirjana Dukaa, Armaghan Soomrob, Frank Tamburrinob, Foad Ghavamib, James Laffertyb
aDepartment of Internal Medicine, Staten Island University Hospital, Staten Island, NY, USA
bDepartment of Cardiology, Staten Island University Hospital, Staten Island, NY, USA
cCorresponding Author: Michael Cinelli, Staten Island University Hospital, 475 Seaview Ave., Staten Island, NY 10305, USA
Manuscript submitted June 14, 2019, accepted July 8, 2019
Short title: Apixaban-Induced Pericardial and Pleural Effusion
doi: https://doi.org/10.14740/cr902
| Abstract | ▴Top |
Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) are used for many conditions where anticoagulation is needed such as non-valvular atrial fibrillation, deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). These novel agents have become popular since they do not require monitoring of therapeutic levels and there is a lower risk of certain bleeding complications when compared to warfarin. However, the efficacy and side effect profile of these agents have not been widely studied in certain patient cohorts, namely cancer patients and patients on immunomodulators or hormone analogs. We present a case of a patient with a history of malignancy and autoimmune disease who developed pericardial and pleural effusions shortly after initiating apixaban for treatment of a PE. In addition, we aim to increase awareness of the role that the newly available reversal agents for anticoagulants would offer in the acute management of hemorrhagic pericardial and pleural effusions caused by DOACs in patients with and without malignancy.
Keywords: Direct acting oral anticoagulant; Pericardial effusion; Cardiac tamponade; Hemopericardium; Cancer; Malignancy; Pulmonary embolism; Venous thromboembolism; Non-valvular atrial fibrillation
| Introduction | ▴Top |
Apixaban is one of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) which act as inhibitors of factor Xa in the coagulation cascade. It has rapid absorption, a 12-h half-life and 25% renal excretion [1, 2]. In the ARISTOTLE study comparing it to warfarin, apixaban significantly reduced the risk of stroke or systemic embolism by 21% and major bleeding by 31% [3]. It is generally favorable over warfarin as patients’ international normalized ratio (INR) does not have to be followed to make dosing adjustments as well as decreased risk of adverse bleeding events [4].
Some of the common causes of hemopericardium include pericarditis, malignancy, infection (particularly tuberculosis), acute myocardial infarction, aortic dissection, cardiac surgery and trauma. It has been reported that anticoagulants predispose patients to develop hemopericardium [5]. This complication may represent a unique DOAC-related complication in subgroups of cancer patients receiving chemotherapy and/or immunotherapy which may result in pharmacodynamic drug-drug interactions [6, 7]. In this report, we present a case of a patient with previous history of gastrointestinal malignancy as well as active autoimmune disease receiving immunotherapy found to have hemorrhagic pericardial and pleural effusions after being initiated on apixaban for a pulmonary embolism (PE).
| Case Report | ▴Top |
A 78-year-old Caucasian woman presented with the complaint of acute-onset shortness of breath associated with right-sided chest pain. She had a past medical history significant for type II diabetes mellitus, hypertension, colon cancer status post colon resection about 18 years ago, subdural hematoma 2 years ago, persistent non-valvular atrial fibrillation, idiopathic thrombotic purpura (currently on romiplostim), combined systolic and diastolic heart failure, pulmonary arterial hypertension and seizure disorder. Her home medications included diltiazem, metoprolol, furosemide, metolazone and levetiracetam. Her weight was 194.2 lb (88.1 kg) and height was 167.6 cm (5 ft 6 in). Her vital signs on arrival were: heart rate of 103 beats per minute, blood pressure of 143/60 mm Hg and temperature of 97.4 °F (26.3 °C). On physical exam, she was not in acute distress and was alert, awake and oriented to person, place and time. Her lungs were clear to auscultation bilaterally and the heart was tachycardic and irregular in rhythm. The patient was noted to have mild bilateral lower extremity edema. Her hemoglobin was 8 g/dL, hematocrit was 25.8% and platelets were 62,000/µL. Prothrombin time (PT) was 11.5 s, INR was 1.06 and activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT) was 25.2 s which were increased from her baseline. The D-dimer level was 659 ng/mL. All other routine lab works including cardiac enzymes were unremarkable. An electrocardiogram (ECG) revealed atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response with a low-voltage QRS and a ventricular rate of 120. Chest X-ray revealed a small left basilar pleural effusion. Computed tomography (CT) angiogram of the chest showed a right lower lobe segmental PE, moderate cardiomegaly and a dilated main pulmonary artery, suggestive of underlying pulmonary arterial hypertension (Fig. 1). Lower extremity duplex was negative for deep vein thrombosis bilaterally. A transthoracic echocardiogram revealed an ejection fraction (EF) of approximately 40%. She was treated with diltiazem 30 mg twice a day and metoprolol tartrate 50 mg two times a day; her arrhythmia subsequently converted to normal sinus rhythm. The patient was placed on a therapeutic-dose of enoxaparin and her symptoms resolved by hospital day 2. The patient was subsequently started on a loading dose of apixaban 10 mg twice a day for 7 days and was discharged with instructions to start a maintenance dose of 5 mg twice a day afterwards as per the package insert guidelines [2].
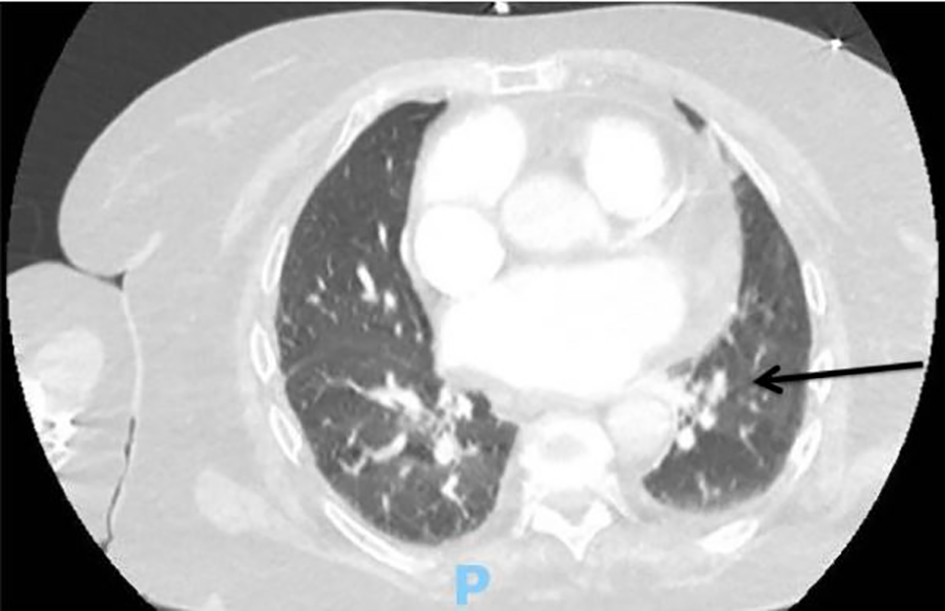 Click for large image | Figure 1. Computed tomography (CT) angiography of the chest upon initial presentation showing a right lower lobe filling defect consistent with segmental pulmonary embolism (black arrow). |
Seven days later, the patient returned to the emergency department with a new onset of progressively worsening shortness of breath which started a day after her hospital discharge. Her vital signs on arrival were within normal limits. Her hemoglobin was 11.3 g/dL, hematocrit was 34.3% and platelet count was 930/µL. She had an INR of 2.33 and prothrombin time of 25.6 s which were elevated compared to previous levels. The troponins were within normal limits and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) was 3,132 pg/mL. Her creatinine was 1.4 mg/dL with a glomerular filtration rate of 36 mL/min/1.73 m2. An ECG revealed atrial fibrillation, left axis deviation, low-voltage QRS with ventricular rate of 89. Chest X-ray although showed persistent left basilar opacity, there was an enlargement of the cardiac silhouette. A bedside echocardiogram was done and revealed similar EF to prior echocardiogram but also revealed a large pericardial effusion. An official transthoracic echocardiogram confirmed the large pericardial effusion without any signs indicative of cardiac tamponade (Fig. 2a). A pericardiocentesis was performed and 300 mL of hemorrhagic fluid was removed and a pericardial catheter was placed. Analysis of the pericardial fluid revealed numerous acute inflammatory cells and no malignant cells, bacteria, fungi or acid fast bacilli. A repeat echocardiogram showed resolution of the pericardial effusion. The pericardial drain was removed and 2 days later the patient decompensated, became septic requiring intubation, pressors and antibiotic therapy. A CT scan of the chest showed a left-sided pleural effusion and a new pericardial effusion (Fig. 2b). A chest tube was subsequently placed and drained 800 mL of fluid. Fluid analysis of the pleural fluid showed cloudy, red fluid with 32,000 red blood cells, 4,843 total nucleated cells, 23% monocyte/macrophage count and 73% segmented granulocytes. The patient was no longer requiring pressors and the chest tube was removed. There was a worsening left pleural effusion and a drainage catheter was placed by cardiothoracic surgery. An echocardiogram 6 days later showed the pericardial effusion to have completely resolved. Apixaban was resumed and the patient was discharged to a skilled nursing facility.
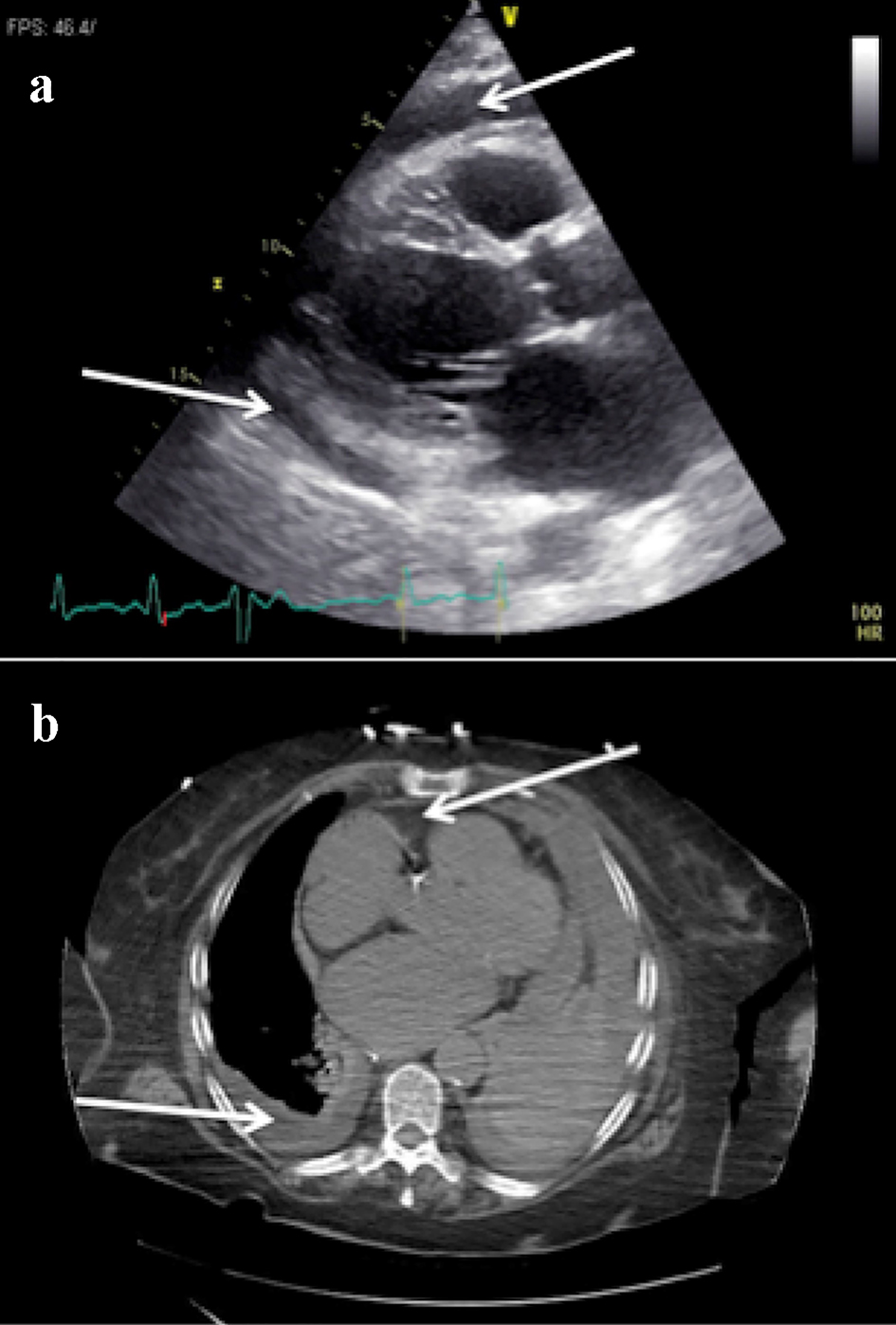 Click for large image | Figure 2. (a) Transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE), parasternal long axis view, showing a new large pericardial effusion (white arrow). (b) Computed tomography (CT) of the chest showing a new pericardial effusion and left-sided pleural effusion (white arrows). |
| Discussion | ▴Top |
Anticoagulants are known to be associated with significant bleeding events. There have been previous case reports of hemopericardium occurring in patients taking warfarin and DOACs [8-11]. As previously mentioned, hemopericardium can also be caused by malignancy. Therefore, it is possible that our patient’s history of malignancy as well as an autoimmune process in the form of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) played a role in the development of this adverse complication of apixaban. It is known that patients with malignancy have a paradoxical increased risk of bleeding in the face of inherent thrombophilia [5]. In a 10-year single-center prospective survey of patients presenting with cardiac tamponade requiring urgent drainage, malignancy accounted for 65% of the primary etiology, and 1-year mortality was 76.5% in patients with malignant disease and 13.3% in those without malignant disease [12]. On rare occasions, cardiac involvement may be the first or only expression of a non-cardiac primary neoplasm [13]. Our patient did not have any evidence of a malignant effusion based on the fluid analysis.
Patients with and without cancer frequently take medications that interact with and alter the pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of other drugs, potentially limiting the safe use of anticoagulant medications [7, 14]. Our patient was taking diltiazem which is a known inhibitor of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 as well as P-glycoprotein. A 1.4-fold increase in apixaban exposure was shown when used concomitantly with diltiazem [6]. This is a concerning finding since blood testing of factor Xa inhibitor levels are not routinely available currently and a normal PT or aPTT are not reliable markers to exclude clinically significant drug levels.
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) guidelines for cancer-associated venous thromboembolism (VTE) state that 6 months of treatment with a low molecular weight heparin (LMWH) is still preferred in patients with proximal VTEs and to prevent recurrences in those with advanced metastatic cancer. But for patients who refuse or have compelling reasons to avoid LMWH, DOACs are acceptable alternatives except in patients with genitourinary or gastrointestinal tract pathology [14]. Another utilization of DOACs has been on thromboprophylaxis in patients with malignancies [15]. A recent randomized controlled trial (RCT) found significantly lower rates of VTE in patients with cancer receiving apixaban versus placebo [16]. Another study found a decreased incidence of VTE and bleeding in high-risk patients with cancer who received rivaroxaban versus placebo [17].
The reversal agent idarucizumab has been successful in the reversal of bleeding including hemopericardium in patients taking dabigatran [10]. Recently the availability of andexanet alfa to reverse the effects of apixaban and rivaroxaban has added a potential solution to the management of patients presenting with bleeding complications such as hemorrhagic pericardial effusions. This agent has been shown to rapidly reverse the anticoagulant effects of direct and indirect (enoxaparin and fondaparinux) factor Xa inhibitors, although no phase three clinical trials or head-to-head trials with usual care are currently available [18].
VTE treatment decisions and ongoing management can be complex due to the risks of bleeding and recurrence of thrombosis. There have been several reports of observed hemopericardium in patients taking DOACs [5, 6, 11, 13]. To our knowledge, this is amongst the few case reports of the complication of spontaneous hemopericardium occurring in a patient on apixaban and the first in a patient with known history of malignancy and autoimmune disease. Studies in this patient population are rare when compared to the reports of bleeding complications in patients without these comorbidities. This is especially true in patients with cancer due to patients’ comorbidities, drug interactions and limited tolerance for oral medications. Our report adds to the growing evidence that DOACs may be associated with major bleeding consequences such as pericardial effusion and tamponade. We recommend that clinicians maintain a high suspicion for hemopericardium in patients who present with acute shortness of breath and/or chest pain shortly after being started on DOACs. There are multiple ongoing or completed clinical trials which evaluated apixaban use in malignancy (clinicaltrials.gov: NCT02581176, NCT02585713, NCT02749617, NCT03895502). These studies will hopefully add to the growing knowledge of this important topic. More studies are also needed to assess the potential role of the reversal agents in the treatment of hemorrhagic pericardial and pleural effusions caused by DOACs.
Acknowledgments
None.
Financial Disclosure
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from the patient.
Author Contributions
ID presented the idea and assisted in the design of the paper. MC and AU performed background search, designed and co-wrote the paper. AS co-wrote and revised the paper. FT, FG and JL provided mentorship and revision of the paper.
| References | ▴Top |
- Frost CE, Byon W, Song Y, Wang J, Schuster AE, Boyd RA, Zhang D, et al. Effect of ketoconazole and diltiazem on the pharmacokinetics of apixaban, an oral direct factor Xa inhibitor. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2015;79(5):838-846.
doi pubmed - Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. Eliquis® (apixaban tablets) Prescribing Information. 2018. Available at: http://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2012/ 202155s000lbl.pdf.
- Granger CB, Alexander JH, McMurray JJ, Lopes RD, Hylek EM, Hanna M, Al-Khalidi HR, et al. Apixaban versus warfarin in patients with atrial fibrillation. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(11):981-992.
doi pubmed - Touma L, Filion KB, Atallah R, Eberg M, Eisenberg MJ. A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of the risk of bleeding with apixaban versus vitamin K antagonists. Am J Cardiol. 2015;115(4):533-541.
doi pubmed - Sigawy C, Apter S, Vine J, Grossman E. Spontaneous hemopericardium in a patient receiving apixaban therapy: First Case Report. Pharmacotherapy. 2015;35(7):e115-117.
doi pubmed - Nassif T, Banchs J, Yusuf S, Mouhayar E. Acute hemorrhagic tamponade in cancer patients receiving direct oral anticoagulant: case series. European Heart Journal. 2017;1:1-4.
doi pubmed - Zhang D, He K, Herbst JJ, Kolb J, Shou W, Wang L, Balimane PV, et al. Characterization of efflux transporters involved in distribution and disposition of apixaban. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41(4):827-835.
doi pubmed - Sablani N, Garg J, Hasan B, Patel R, Martinez MW. First reported case series in the United States of hemopericardium in patients on apixaban. HeartRhythm Case Rep. 2018;4(2):82-84.
doi pubmed - Basnet S, Tachamo N, Tharu B, Dhital R, Ghimire S, Poudel D. Life-threatening hemopericardium associated with Rivoroxaban. Case Reports in Cardiology. 2017;2017:1-3.
doi pubmed - Song S, Cook J, Goulbourne C, Meade M, Salciccioli, Lazar J. First reported case report of hemopericardium related to dabigatran use reversed by new antidote Idarucizumab. Case Rep Cardiol. 2017;2017:6458636.
doi pubmed - Ertas F, Polat N, Yildiz A, Oylumlu M, Ulgen MS. Anticoagulant-induced hemopericardium with tamponade: A case report and review of the literature. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Investigations. 2013;4:229-233.
doi - Cornily JC, Pennec PY, Castellant P, Bezon E, Le Gal G, Gilard M, Jobic Y, et al. Cardiac tamponade in medical patients: a 10-year follow-up survey. Cardiology. 2008;111(3):197-201.
doi pubmed - Hsi DH, Krishnamurthy M, Ryan GF, Luo P, Woodlock TJ. Successful management of hemopericardium and cardiac tamponade secondary to occult malignancy and anticoagulation. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2010;15(2):e33-35.
- Soff GA. Use of Direct Oral Anticoagulants for Treating Venous Thromboembolism in Patients With Cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2018;16(5S):670-673.
doi pubmed - Lyman GH, Bohlke K, Khorana AA, Kuderer NM, Lee AY, Arcelus JI, Balaban EP, et al. Venous thromboembolism prophylaxis and treatment in patients with cancer: american society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline update 2014. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33(6):654-656.
doi pubmed - Carrier M, Abou-Nassar K, Mallick R, Tagalakis V, Shivakumar S, Schattner A, Kuruvilla P, et al. Apixaban to Prevent Venous Thromboembolism in Patients with Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(8):711-719.
doi pubmed - Khorana AA, Soff GA, Kakkar AK, Vadhan-Raj S, Riess H, Wun T, Streiff MB, et al. Rivaroxaban for thromboprophylaxis in high-risk ambulatory patients with cancer. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(8):720-728.
doi pubmed - Andexxa-an antidote for apixaban and rivaroxaban. JAMA. 2018;320(4):399-400.
doi pubmed
This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial 4.0 International License, which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Cardiology Research is published by Elmer Press Inc.


