| Age | 0.38*** | -0.09 |
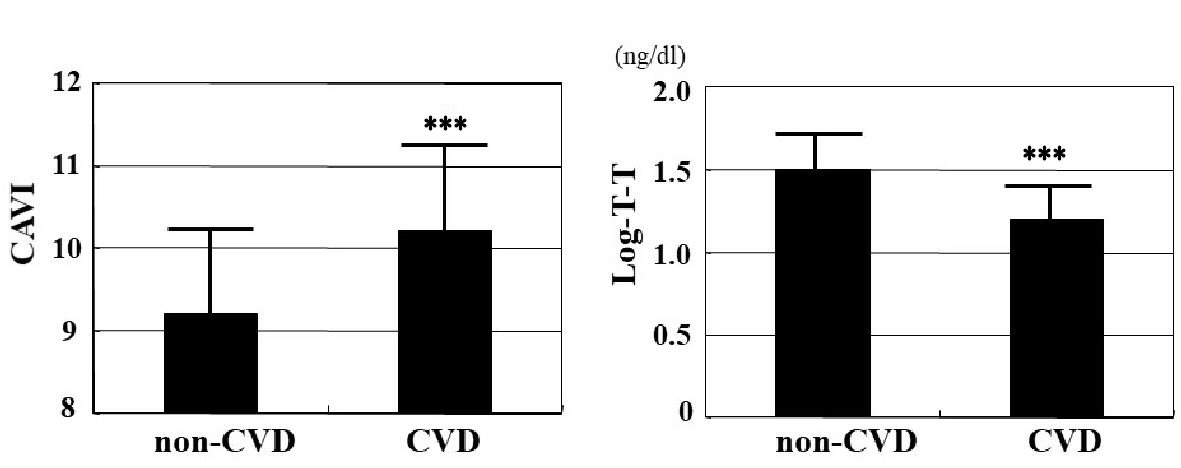
| CVD (Yes = 1, No = 0) | 0.40*** | -0.43*** |
| Body mass index | 0.03 | -0.07 |
| Current smoker (Yes = 1, No = 0) | 0.05 | -0.02 |
| Hypertension (Yes = 1, No = 0) | 0.15* | -0.14* |
| Systolic BP | 0.14* | -0.13* |
| Diastolic BP | 0.09 | -0.08 |
| Dyslipidemia (Yes = 1, No = 0) | 0.06 | -0.03 |
| Total cholesterol | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| LDL cholesterol | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Triglyceride | 0.08 | 0.11 |
| HDL cholesterol | -0.04 | -0.07 |
| FBG | 0.09 | 0.1 |
| HOMA-IR | 0.12 | -0.15* |
| HbA1c | 0.14* | -0.21*** |
| Skin AF | 0.32*** | -0.22*** |
| Log- hs-CRP | 0.32*** | -0.25*** |
| d-ROMs test | 0.33*** | -0.43*** |
| Detection of E2 (Yes = 1, No = 0) | -0.20** | 0.47*** |
| E2 | -0.13* | 0.19** |
| Sulfonylurea (Yes = 1, No = 0) | 0.09 | 0.08 |
| Biguanide (Yes = 1, No = 0) | 0.03 | 0.07 |
| DPP-4 inhibitor (Yes = 1, No = 0) | -0.06 | 0.05 |
| Insulin (Yes = 1, No = 0) | 0.1 | 0.06 |
| RAS inhibitor (Yes = 1, No = 0) | -0.07 | 0.03 |
| Statin (Yes = 1, No = 0) | -0.06 | 0.04 |