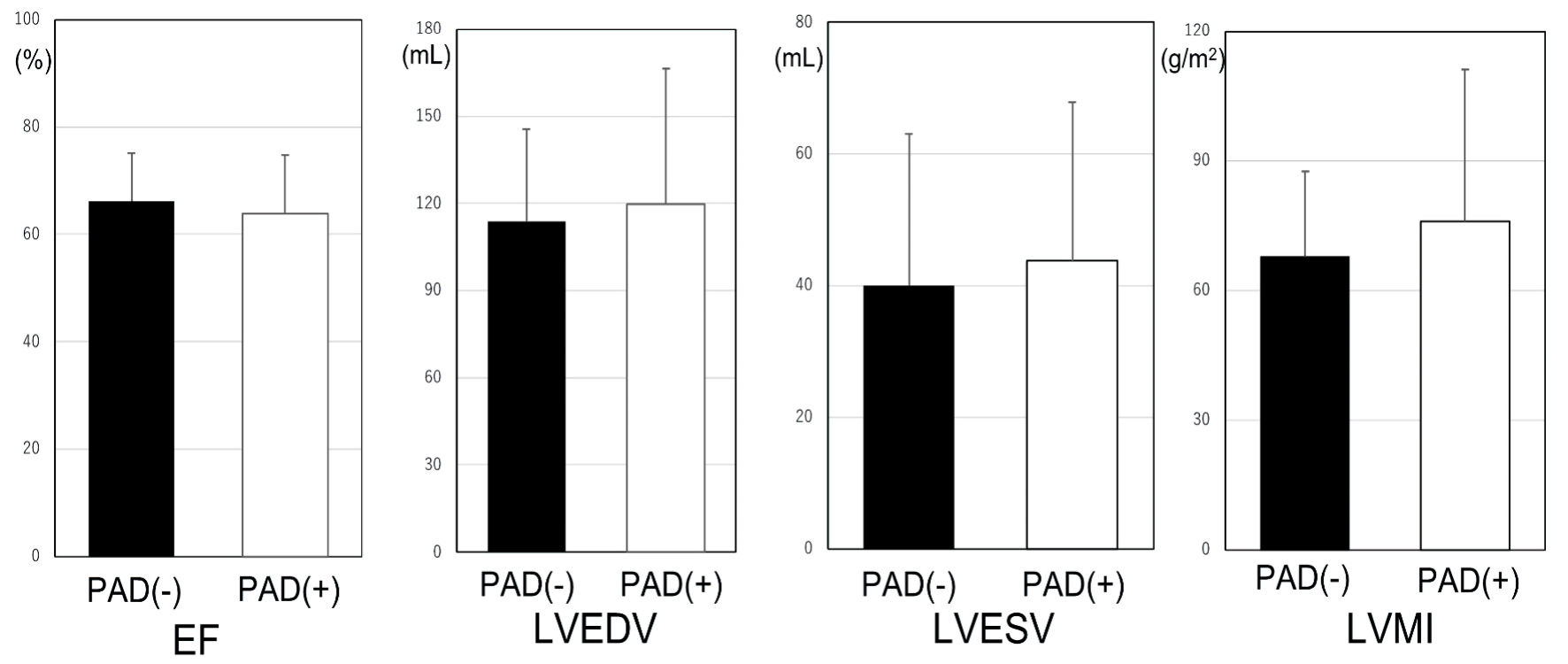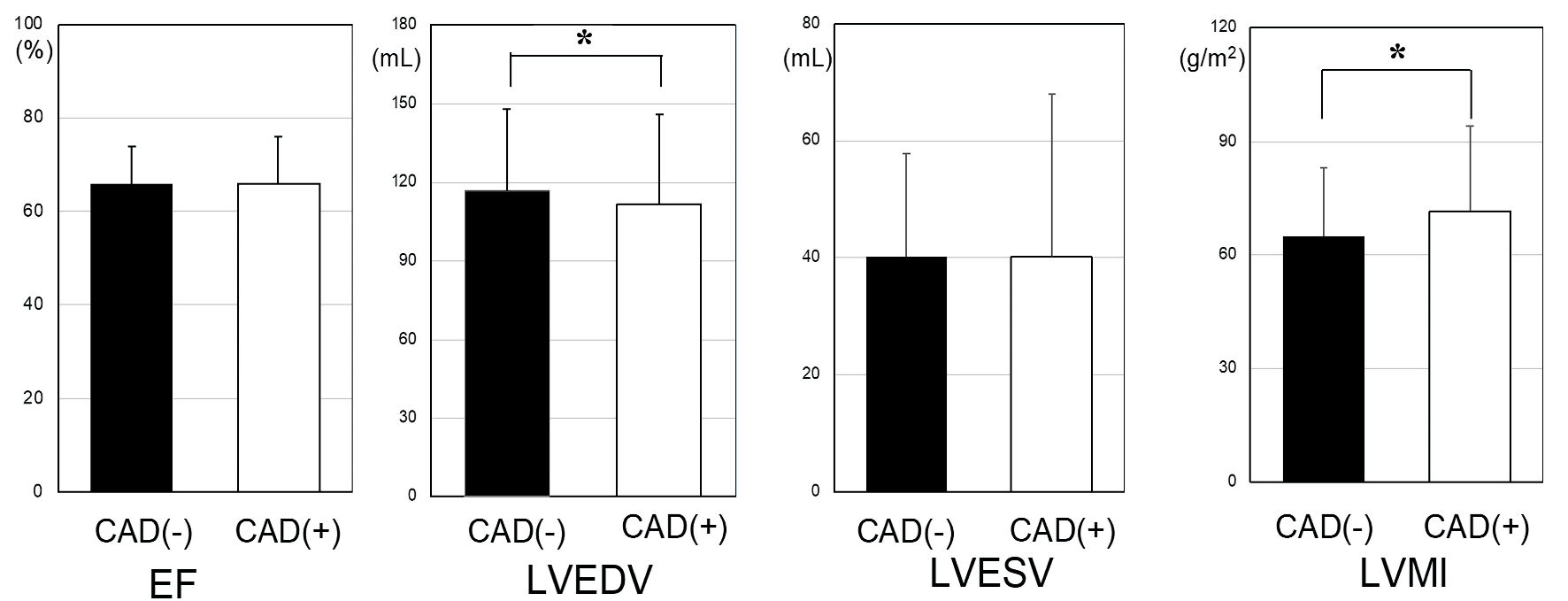
Figure 1. LV profiles in the non-CAD and CAD groups. *P < 0.05. CAD: coronary artery disease; LV: left ventricular; LVMI: left ventricular mass index; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; LVEDV: left ventricular end-diastolic volume; LVESV: left ventricular end-systolic volume.