Figures
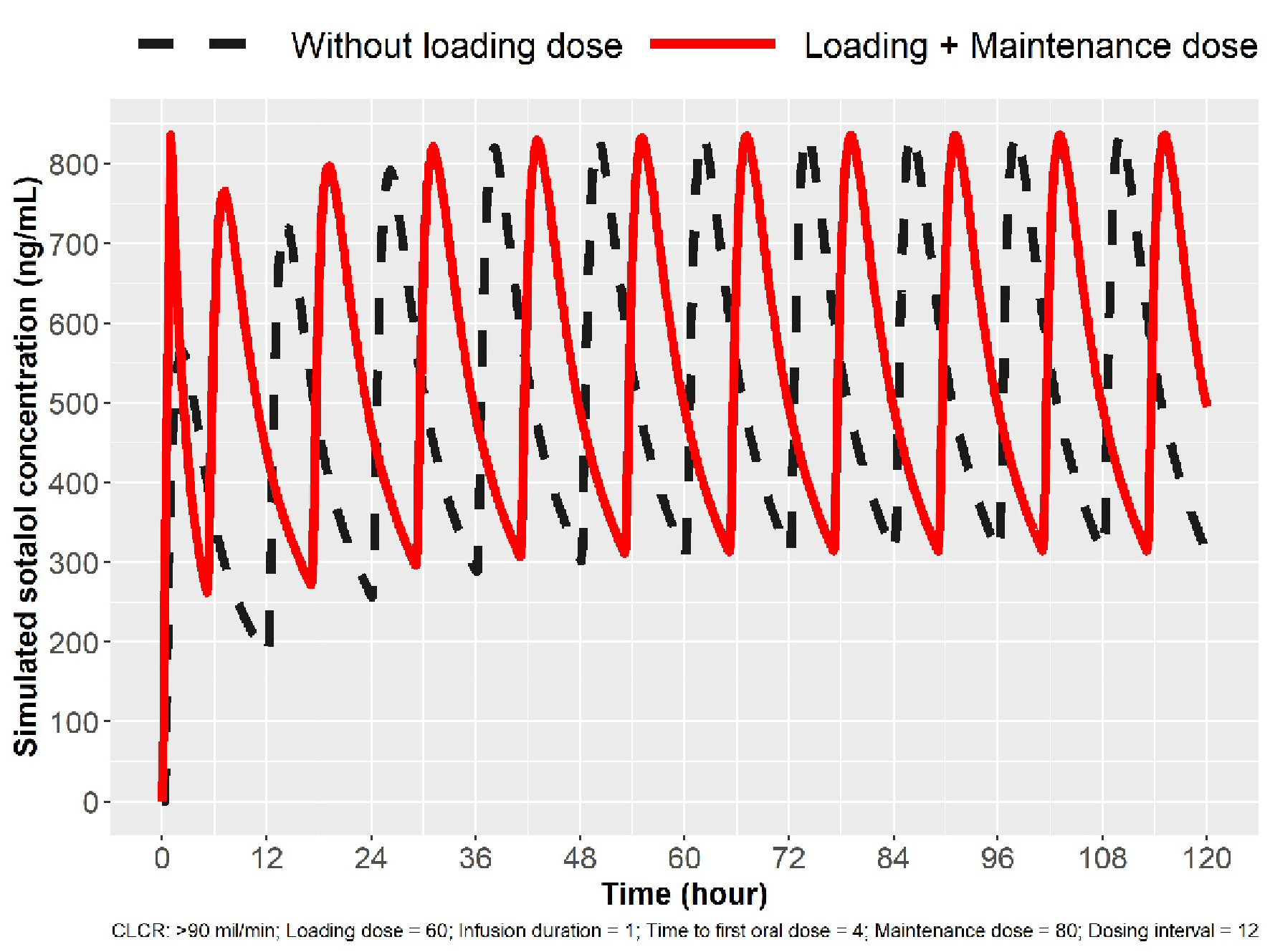
Figure 1. Simulation for 80 mg loading in patients with normal renal function (ClCr > 90 mL/min). The broken line indicates sotalol concentrations with oral (PO) dosing. The solid line indicates sotalol concentrations following IV loading, and Cmax ss concentration can be obtained in 1 h and three Cmax peaks in 24 h. IV: intravenous; ClCr: creatinine clearance.
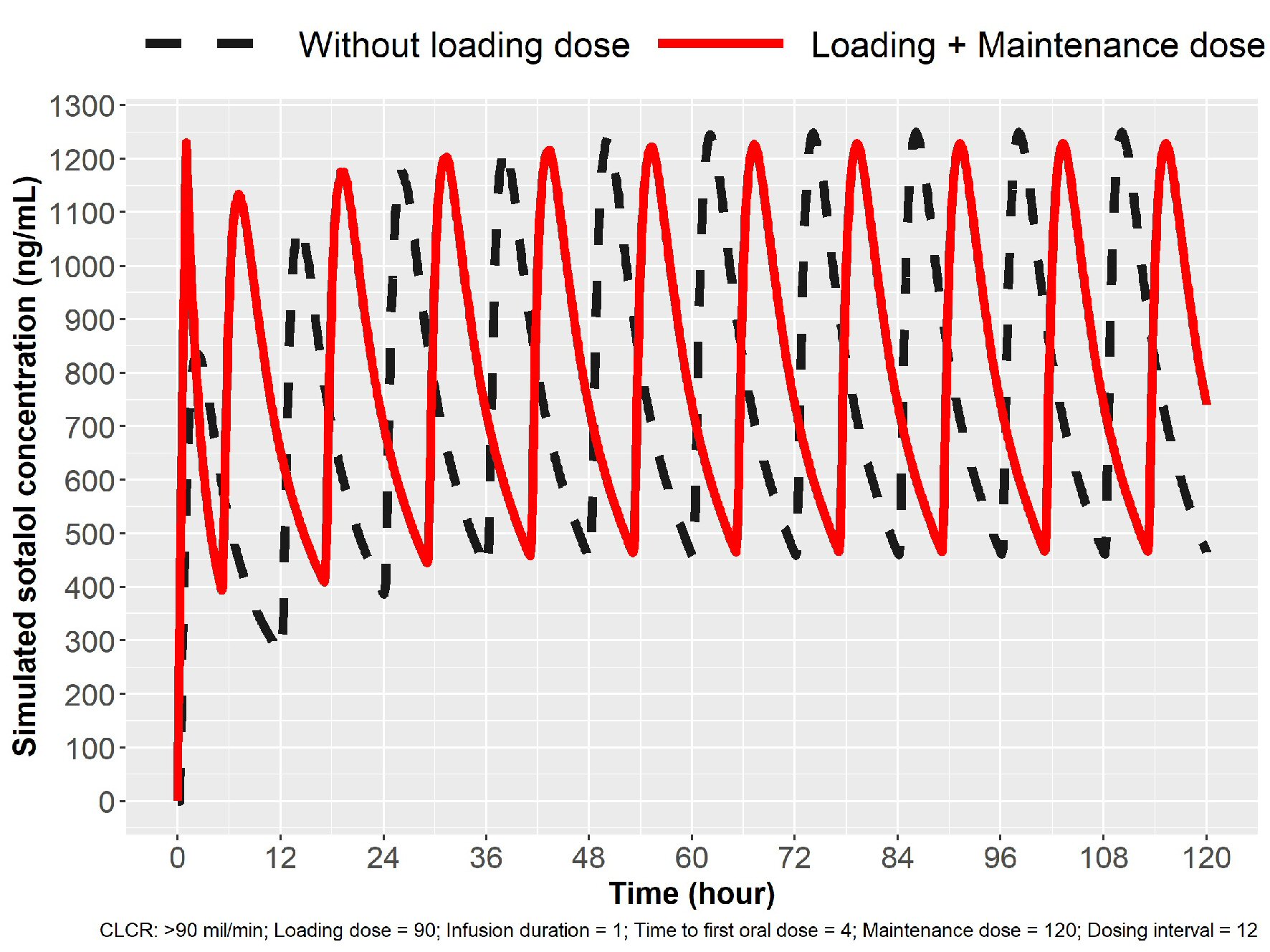
Figure 2. Simulation for 120 mg loading in patients with normal renal function (ClCr > 90 mL/min). Oral dosing 120 mg sotalol every 12 h (broken line) and IV loading 90 mg over 1 h followed by oral dosing. Cmax ss was obtained in 1 h with IV loading. IV: intravenous; ClCr: creatinine clearance.
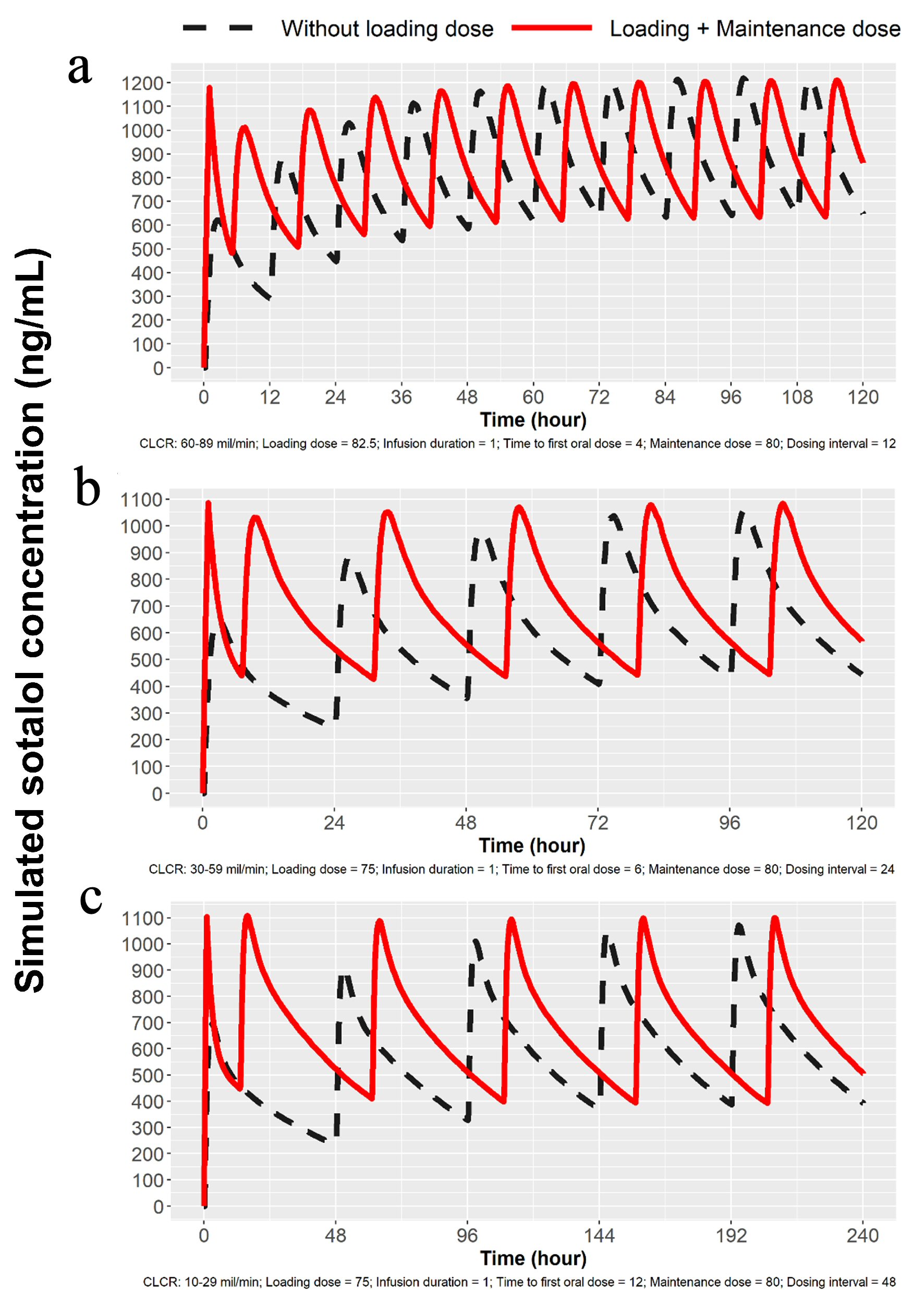
Figure 3. Simulations for 80 mg dosing for patients with mild, moderate and severe renal impairment. (a) Simulation with mild renal impairment (ClCr: 60 - 89 mL/min). Oral loading broken lines and solid line with 82.5 mg IV load. (b) Simulation for moderate renal impairment (ClCr: 30 - 59 mL/min). Broken line indicates oral loading and solid line 75 mg IV load, followed by 80 mg PO at 7 h and then 80 mg PO every 24 h. (c) Simulation for severe renal impairment (ClCr: 10 - 29 mL/min). Broken line indicates oral loading 80 mg PO every 48 h, while solid line represents 75 mg IV followed by 80 mg PO at 13 h and then every 48 h thereafter. IV: intravenous; ClCr: creatinine clearance; PO: oral.
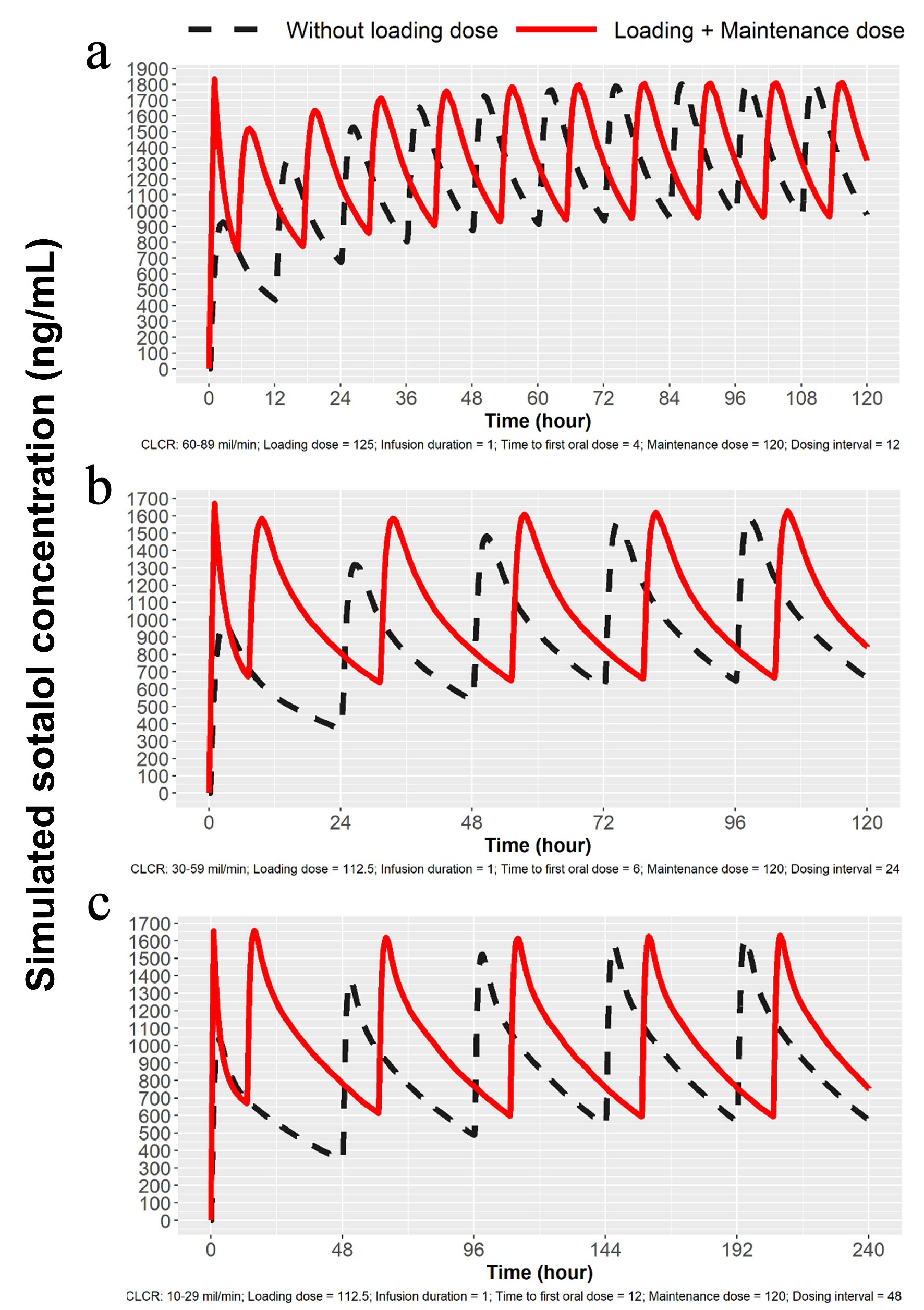
Figure 4. Simulations for 120 mg dosing for patients with mild, moderate and severe renal impairment. (a) Simulation for mild renal impairment (ClCr: 60 - 89 mL/min). Broken line represents 120 mg sotalol PO every 12 h and the solid line represents 125 mg IV load over 1 h followed by 120 mg at 5 h PO and then every 12 h thereafter. (b) Simulation for moderate renal impairment (ClCr: 30 - 59 mL/min). Broken line represents 120 mg sotalol PO administered every 24 h and solid line represents 112.5 mg IV over 1 h followed by 120 mg at 7 h and then 120 mg PO every 24 h. (c) Simulation for severe renal impairment (ClCr: 10 - 29 mL/min). Broken line represents120 mg sotalol orally every 48 h and the solid line 112.5 mg IV over 1 h followed by 120 mg orally at 13 h and then 120 mg PO every 48 h. IV: intravenous; ClCr: creatinine clearance; PO: oral.
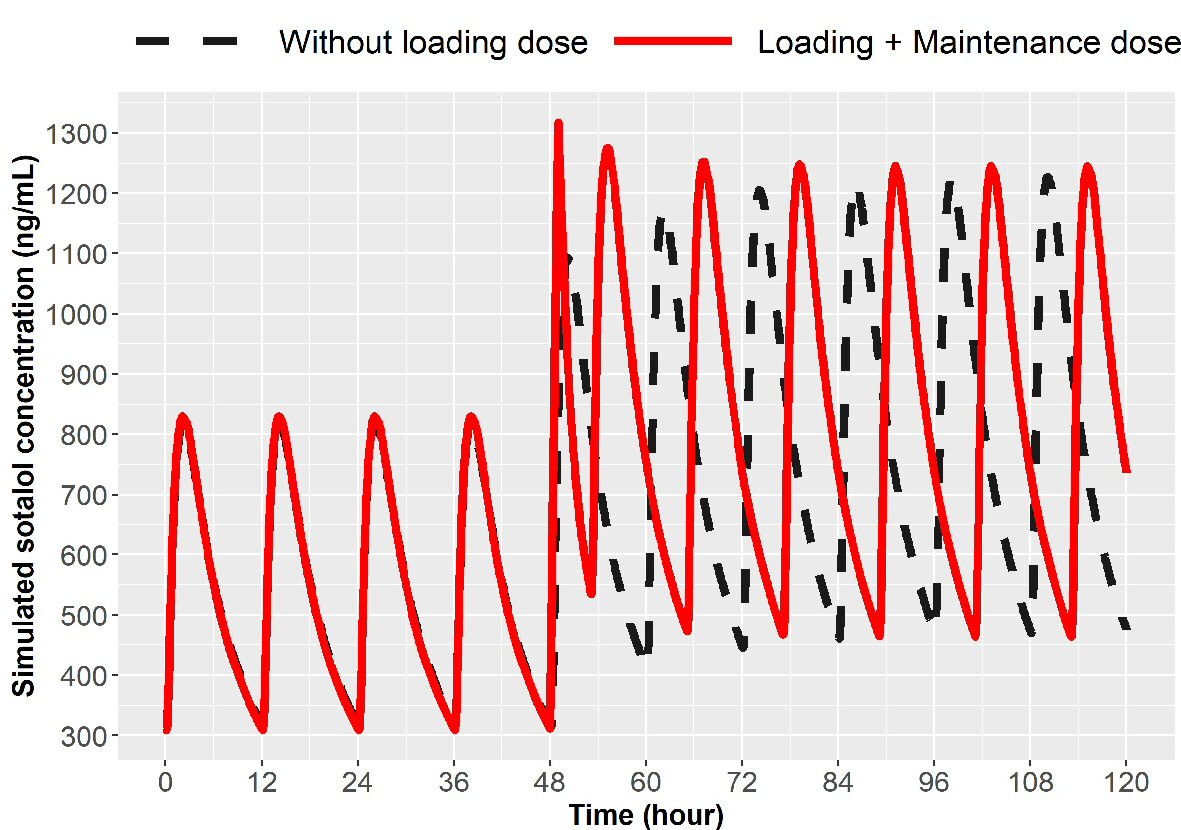
Figure 5. Simulation for dose escalation from 80 to 120 mg in patients with normal renal function (ClCr > 90 mL/min). Broken line represents oral loading, 120 mg every 12 h and the solid line represents 75 mg IV over 1 h given at 12 h after the last 80 mg PO dose followed by 120 mg oral at 5 h and then every 12 h thereafter. IV: intravenous; ClCr: creatinine clearance; PO: oral.
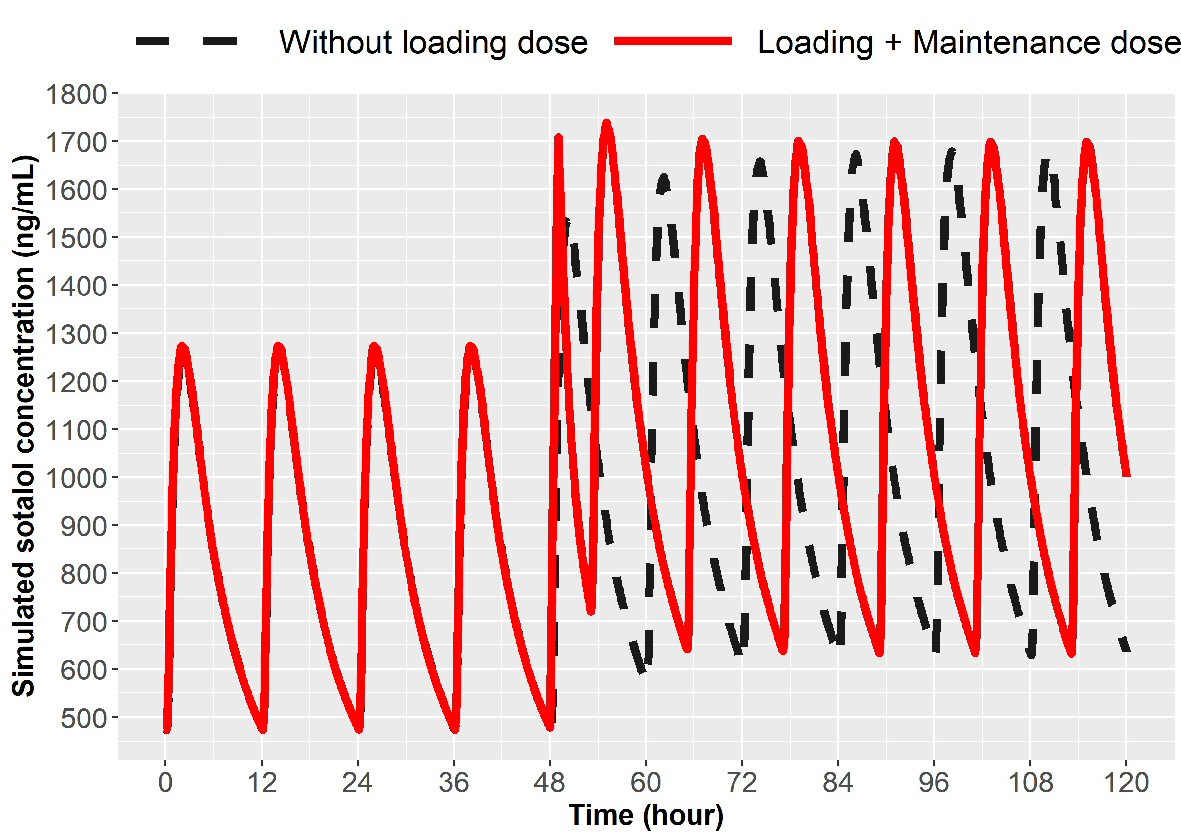
Figure 6. Simulation for dose escalation from 120 to 160 mg in patients with normal renal function (ClCr > 90 mL/min). The broken line represents 160 mg PO sotalol 12 h after the last 120 mg PO dose and then 160 mg at every 12 h thereafter. The solid line represents 90 mg IV sotalol loading over 1 h given 12 h after the last 120 mg dose followed by 160 mg PO at 5 h and then every 12 h thereafter. IV: intravenous; ClCr: creatinine clearance; PO: oral.
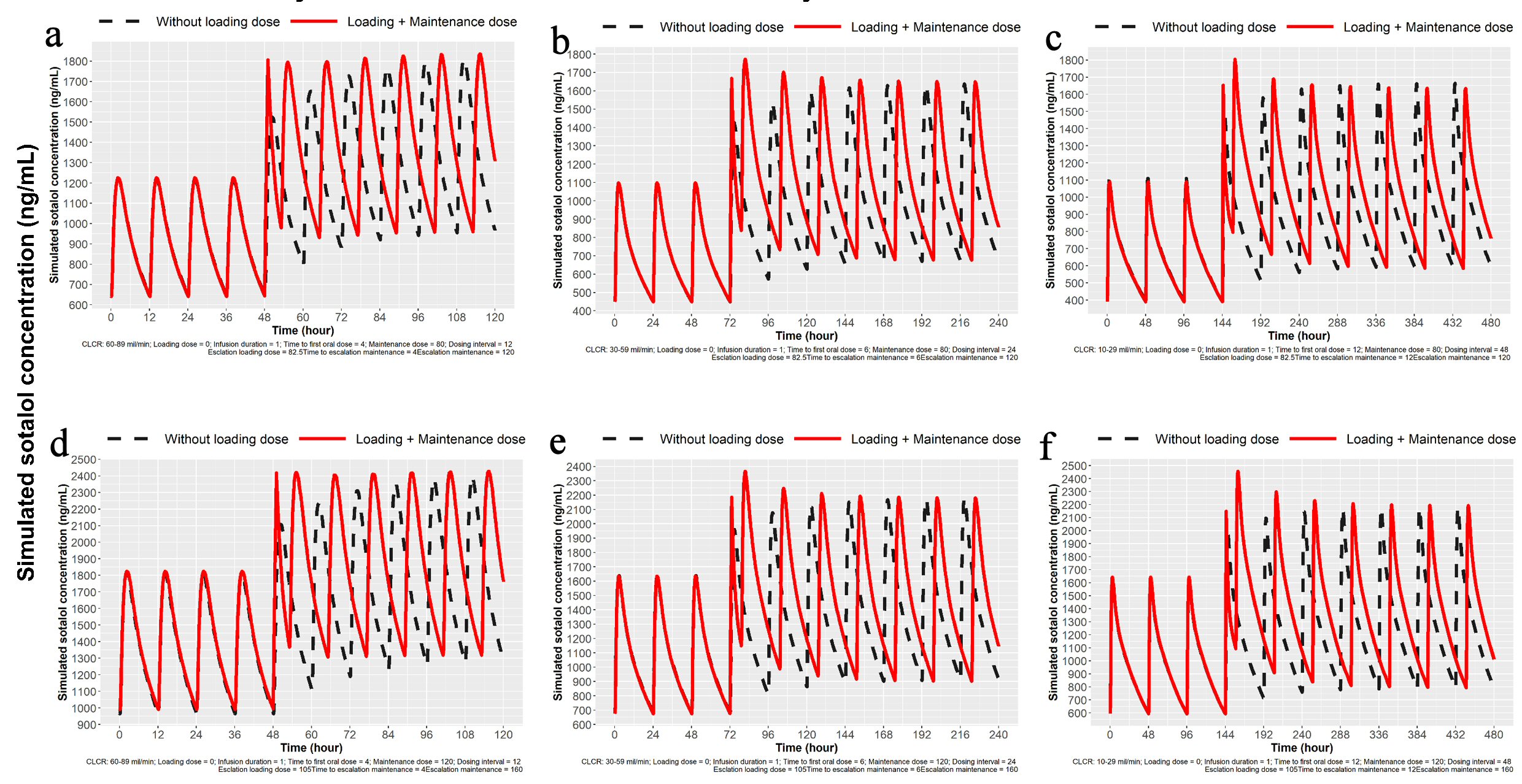
Figure 7. Simulation for dose escalation from 80 to 120 mg and from 120 to 160 mg sotalol for patients with mild, moderate and severe impairment of renal function. (a) Simulation for dose escalation from 80 to 120 mg in patients with mild renal impairment (ClCr: 60 - 89 mL/min). Oral loading 120 mg PO at 12 h after the last 80 mg PO dose and then 120 mg every 12 h. IV loading 82.5 mg IV load over 1 h, 12 h after the last 80 mg PO dose followed by 120 mg at 5 h and then 120 mg PO every 12 h. (b) Simulation for moderate renal impairment (ClCr: 30 - 59 mL/min). Oral loading 120 mg sotalol PO at 24 h after the last 80 mg PO dose and then every 24 h. IV loading 82.5 mg over 1 h at 12 h after the last 80 mg PO dose followed by 120 mg at 7 h and then every 24 h. (c) Simulation for severe renal impairment (ClCr: 10 - 29 mL/min). Oral loading 120 mg sotalol oral 48 h after the last 80 mg PO dose and then 120 mg every 48 h. IV loading of 82.5 mg IV over 1 h at 48 h after the last 80 mg PO dose followed by 120 mg PO at 13 h and then every 48 h. (d) Simulation for dose escalation from 120 to 160 mg in patients with mild renal impairment (ClCr: 60 - 89 mL/min). Oral loading 160 mg sotalol PO at 12 h after the last 120 mg PO dose and then 160 mg at every 12 h. IV loading of 90 mg IV over 1 h at 12 h after the last 120 mg PO dose followed by 160 mg PO at 5 h from the start of the infusion and then 160 mg PO every 12 h. (e) Simulation for moderate renal impairment (ClCr: 30 - 59 mL/min). Oral loading 160 mg sotalol at 24 h after the last 120 mg PO dose and then 160 mg PO every 24 h. IV loading of 105 mg IV load administered over 1 h at 24 h after the last 120 mg PO dose followed by 160 mg PO at 7 h and then 160 mg PO every 24 h. (f) Simulation for severe renal impairment (ClCr: 10 - 29 mL/min). Oral loading 160 mg sotalol at 48 h after the last 120 mg PO dose and then 160 mg every 48 h. IV loading of 105 mg IV over 1 h at 48 h after the last 120 mg PO dose followed by 160 mg PO at 13 h and then 160 mg PO every 48 h. IV: intravenous; ClCr: creatinine clearance; PO: oral.
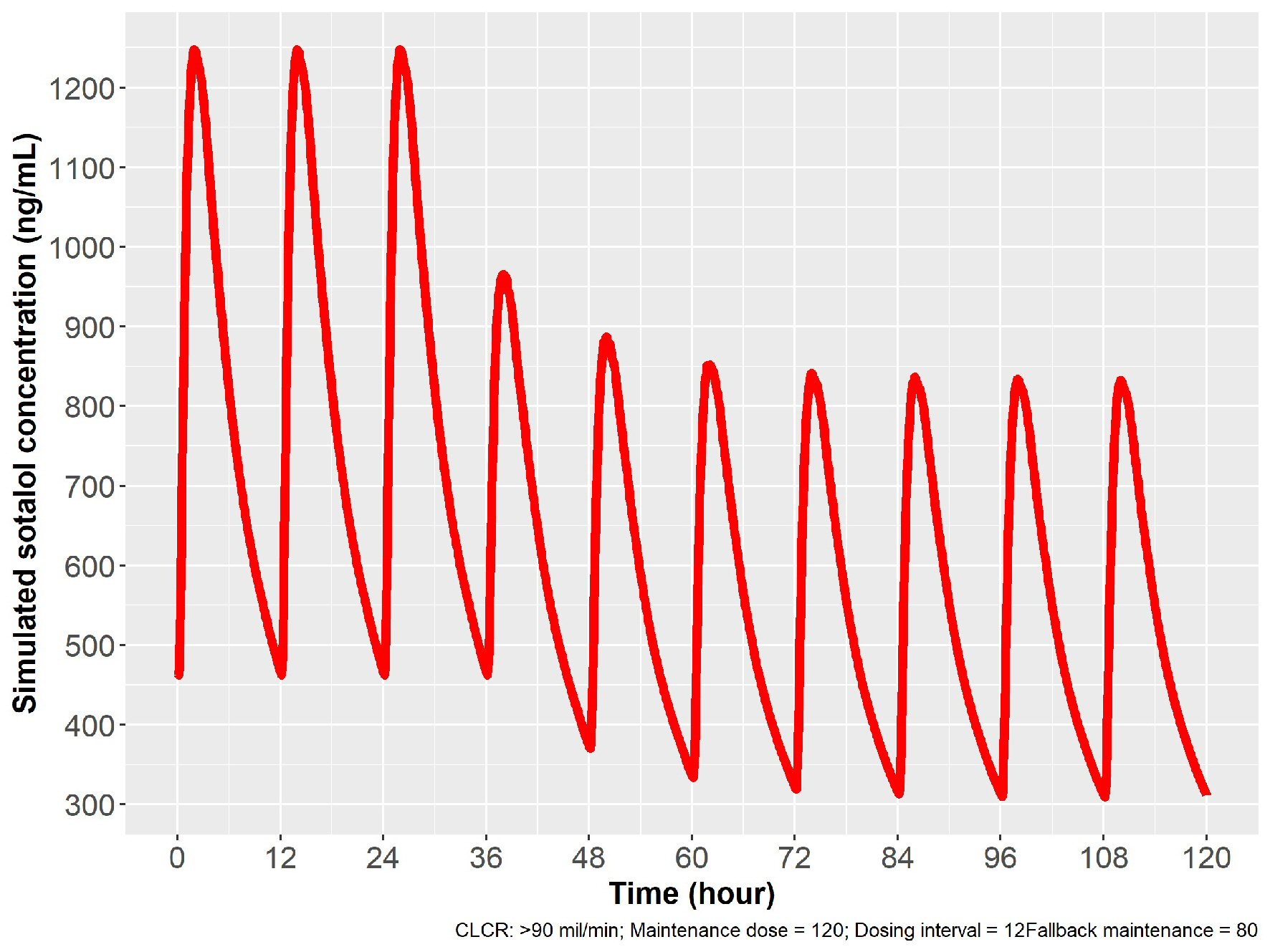
Figure 8. Simulation for dose reduction from 120 to 80 mg PO sotalol in patients with normal renal function (ClCr: 90 mL/min). After 12 h from the last 120 mg dose, 80 mg PO given with a new steady state achieved in 24 h, with 80 mg given every 12 h. ClCr: creatinine clearance; PO: oral.
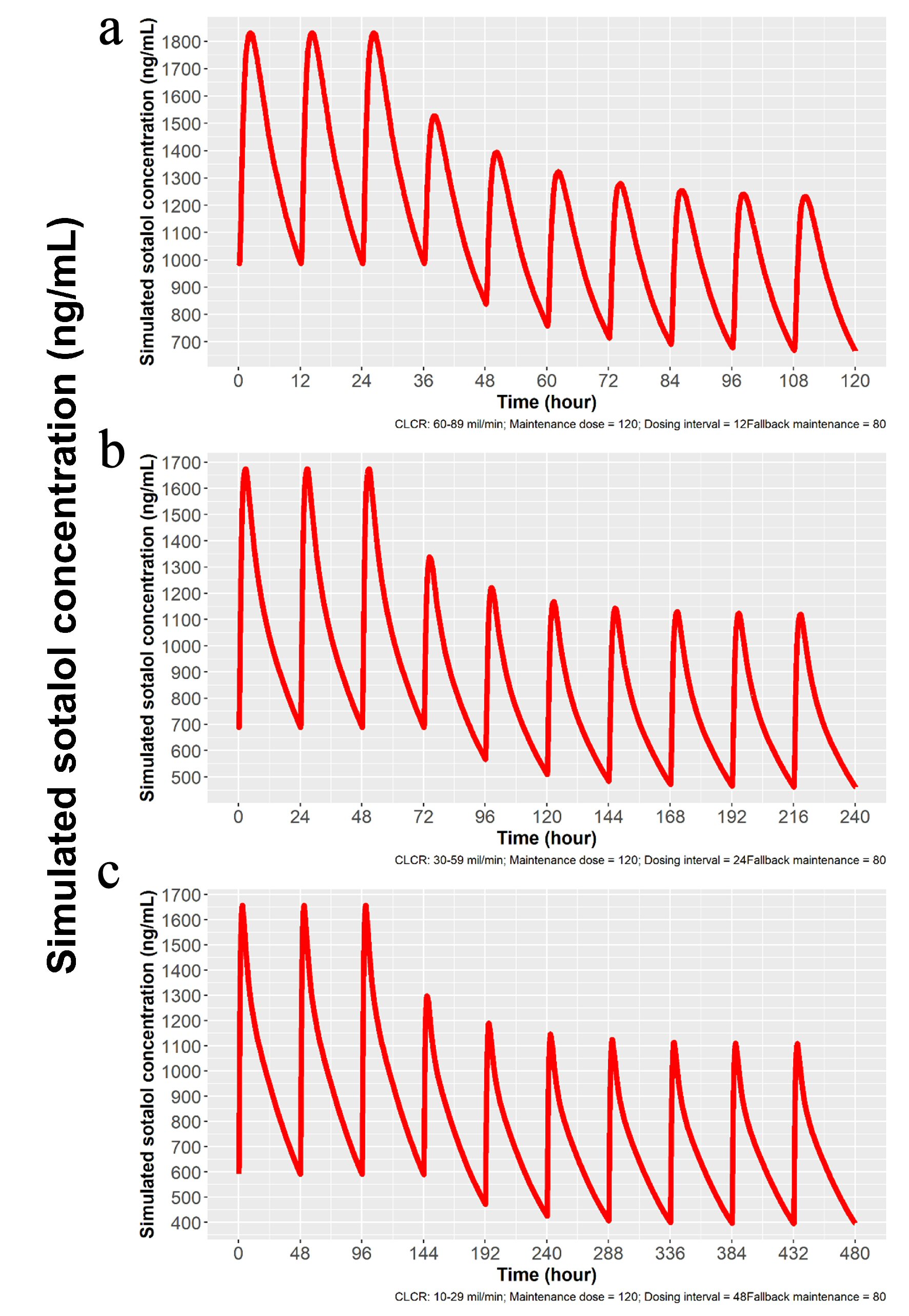
Figure 9. Simulation for dose reduction from 120 to 80 mg PO sotalol for patients with mild, moderate and severe impairment of renal function. (a) Simulation for patients with mild renal impairment (ClCr: 60 - 89 mL/min). After the last 120 mg dose, 80 mg is given in 12 h, and a new steady state is achieved in 48 h, with 80 mg dosing every 24 h thereafter. (b) Simulation for patients with moderate renal impairment (ClCr: 30 - 59 mL/min). Twenty-four hours after the last 120 mg dose, 80 mg is given and new steady state is reached in 72 h with 80 mg dosing every 24 h. (c) Simulation for patients with severe renal impairment (ClCr: 10 - 29 mL/min). Forty-eight hours after stopping the last dose of 120 mg, a dose of 80 mg is given and a new steady state is obtained in 96 h, with 80 mg dosing every 48 h thereafter. ClCr: creatinine clearance; PO: oral;
Table
Table 1. Recommended Loading Dosages for Initiation and Dose Escalation of Sotalol Administration
| ClCra (mL/min) | IV loading dose (mg) to be administered over 1 h when the oral dose is going from | Minimum delay to first oral dose (h) | Oral dosing interval (h) |
|---|
| Sotalol initiation | Sotalol escalation |
|---|
| 0 - 80 mgb | 0 - 120 mg | 80 - 120 mg | 120 - 160 mg |
|---|
| aCalculated using Cockcroft-Gault formula. bRecommended starting dose. ClCr: creatinine clearance; IV: intravenous. |
| > 90 | 60 | 90 | 75 | 90 | 4 | 12 |
| 60 - 90 | 82.5 | 125 | 82.5 | 105 | 4 | 12 |
| 30 - 60 | 75 | 112.5 | 82.5 | 105 | 6 | 24 |
| 10 - 30 | 75 | 112.5 | 82.5 | 105 | 12 | 48 |








