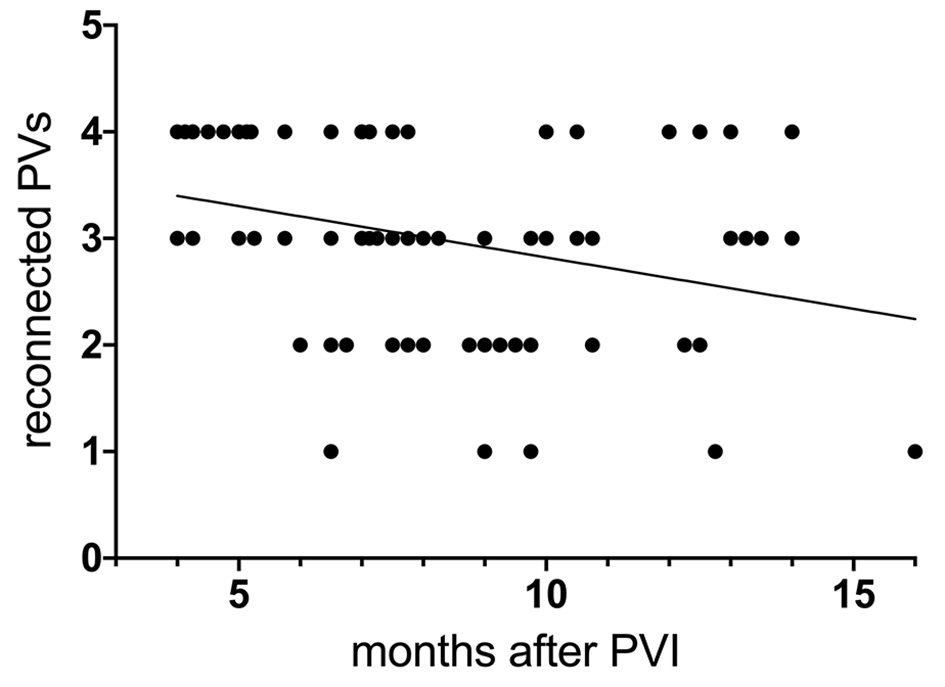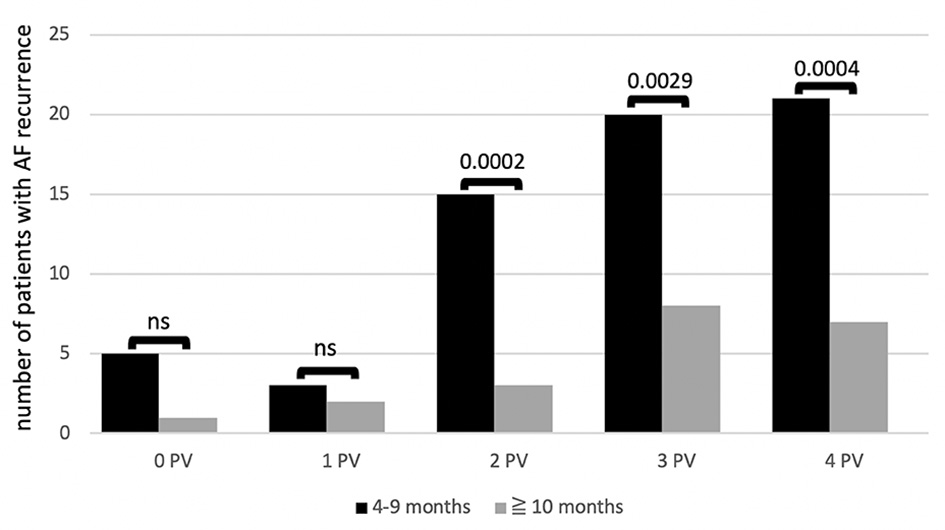
Figure 1. Number of patients with recurrence of AF during follow-up depending on number of reconnected PVs (0 - 4) found at redo PVI at different time intervals: early recurrence (black column) versus late recurrence (grey column). P values above each column. Left common trunk counted as one PV. AF: atrial fibrillation; ns: not significant: PV: pulmonary vein; PVI: pulmonary vein isolation.