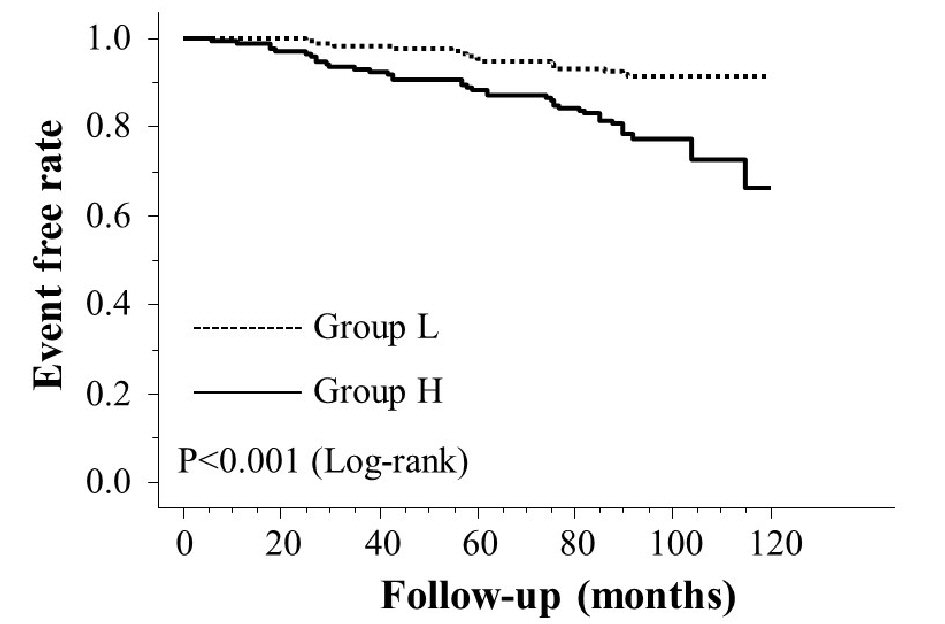
Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier curve for the incidence of heart failure hospitalization.
| Cardiology Research, ISSN 1923-2829 print, 1923-2837 online, Open Access |
| Article copyright, the authors; Journal compilation copyright, Cardiol Res and Elmer Press Inc |
| Journal website https://www.cardiologyres.org |
Original Article
Volume 9, Number 3, June 2018, pages 153-160
Efficacy of the Reactive Oxygen Metabolite Test as a Predictor of Initial Heart Failure Hospitalization in Elderly Patients With Chronic Heart Failure
Figures

Tables
| Overall | Group L | Group H | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous values are mean ± SD. D-ROMs: derivatives of reactive oxygen metabolites; IVSTd: interventricular septal thickness at end-diastole; LVDd: left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; LAD: left atrial dimension; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; hs-CRP: high sensitivity C reactive protein; CAVI: cardio-ankle vascular index; RAS: renin-angiotensin system. | ||||
| N (Male/female) | 428 (108/320) | 214 (58/156) | 214 (50/164) | 0.375 |
| Age (yrs) | 75 ± 7 | 74 ± 6 | 76 ± 8 | 0.108 |
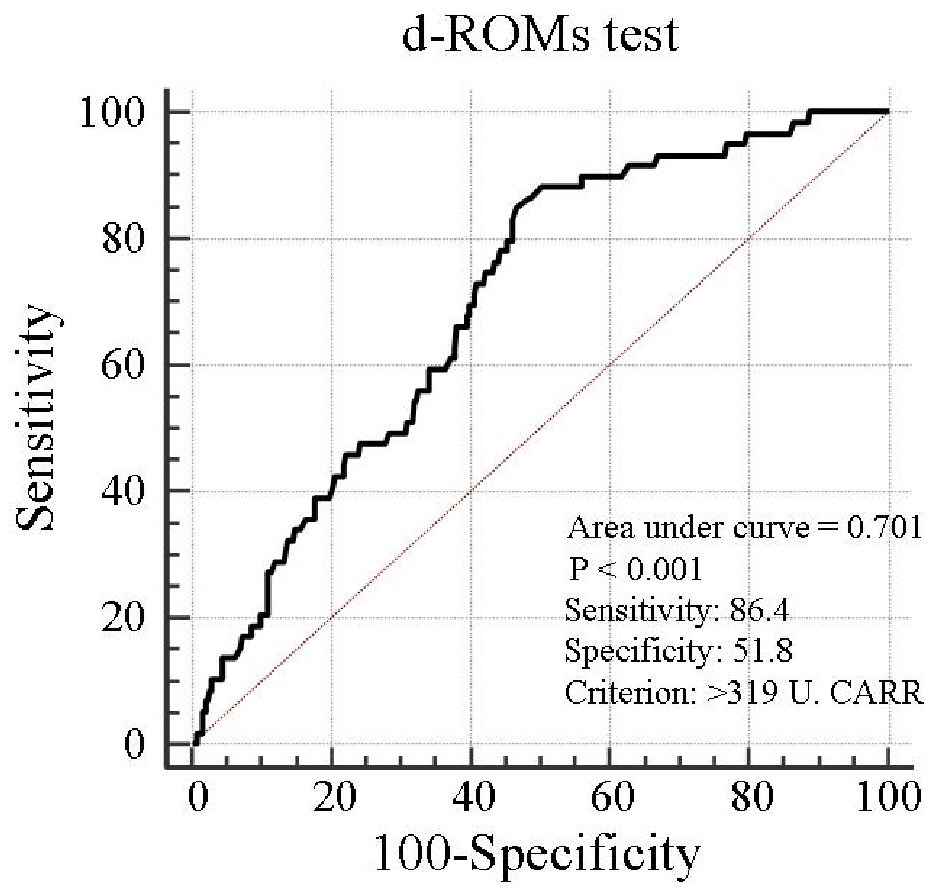
| D-ROMs test (U. CARR) | 328 ± 116 | 235 ± 45 | 421 ± 85 | < 0.001 |
| Body mass index | 22.8 ± 3.5 | 22.9 ± 3.4 | 22.8 ± 3.6 | 0.546 |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 99 (23) | 46 (21) | 53 (25) | 0.423 |
| Ischemic heart disease, n (%) | 70 (16) | 31 (14) | 39 (18) | 0.396 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 316 (74) | 156 (73) | 160 (75) | 0.584 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 144 ± 24 | 144 ± 21 | 144 ± 27 | 0.852 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 86 ± 11 | 86 ± 11 | 86 ± 10 | 0.695 |
| Pulse rate (/min) | 65 ± 13 | 64 ± 12 | 66 ± 14 | 0.363 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 224 (52) | 102 (48) | 122 (57) | 0.051 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 105 (25) | 24 (11) | 81 (38) | < 0.001 |
| Hear valvular disease, n (%) | 318 (74) | 156 (73) | 162 (76) | 0.585 |
| IVSTd (mm) | 9.5 ± 1.6 | 9.4 ± 1.5 | 9.7 ± 1.7 | 0.059 |
| LVDd (mm) | 48 ± 4 | 48 ± 3 | 48 ± 4 | 0.529 |
| LVEF (%) | 67.8 ± 11.7 | 67.4 ± 12.1 | 68.3 ± 11.3 | 0.3 |
| LAD (mm) | 42 ± 6 | 42 ± 6 | 43 ± 6 | 0.421 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.7 ± 1.6 | 12.8 ± 1.6 | 12.7 ± 1.5 | 0.592 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2 ) | 55.2 ± 22.2 | 55.6 ± 22.4 | 54.8 ± 21.9 | 0.742 |
| Log-BNP (pg/mL) | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 1.9 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 0.3 | < 0.01 |
| hs-CRP (mg/dL) | -1.2 ± 0.5 | -1.3 ± 0.5 | -1.1 ± 0.5 | < 0.05 |
| CAVI | 9.5 ± 1.2 | 9.3 ± 1.2 | 9.8 ± 1.2 | < 0.001 |
| Medication | ||||
| RAS inhibitor, n (%) | 269 (63) | 134 (63) | 135 (63) | 0.92 |
| β-blocker, n (%) | 74 (17) | 43 (20) | 31 (15) | 0.126 |
| Diuretics, n (%) | 87 (20) | 50 (23) | 37 (17) | 0.12 |
| Statin, n (%) | 119 (28) | 61 (29) | 58 (27) | 0.789 |
| Non HF hospitalization (n = 370) | HF hospitalization (n = 58) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous values are mean ± SD. HF: heart failure; IVSTd: interventricular septal thickness at end- diastole; LVDd: left ventricular end-diastolic diameter; LVEF: left ventricular ejection fraction; LAD: left atrial dimension; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; hs-CRP: high sensitivity C reactive protein; CAVI: cardio-ankle vascular index; RAS: renin-angiotensin system. | |||
| Male/female | 96/274 | 12/46 | 0.393 |
| Age (yrs) | 74 ± 7 | 79 ± 7 | < 0.001 |
| Body mass index | 22.9 ± 3.4 | 22.7 ± 3.8 | 0.679 |
| Current smoker, n (%) | 78 (21) | 21 (36) | < 0.05 |
| Ischemic heart disease, n (%) | 58 (16) | 12 (21) | 0.234 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 271 (73) | 45 (78) | 0.675 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 144 ± 24 | 141 ± 25 | 0.397 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mm Hg) | 86 ± 10 | 85 ± 11 | 0.676 |
| Pulse rate (/min) | 65 ± 13 | 67 ± 13 | 0.391 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 188 (51) | 36 (62) | 0.111 |
| Diabetes mellitus, n (%) | 82 (22) | 23 (40) | < 0.01 |
| Hear valvular disease, n (%) | 274 (74) | 44 (76) | 0.899 |
| IVSTd (mm) | 9.5 ± 1.6 | 9.7 ± 2.1 | 0.386 |
| LVDd (mm) | 48 ± 3 | 49 ± 5 | 0.217 |
| LVEF (%) | 67.7 ± 11.8 | 68.0 ± 11.5 | 0.359 |
| LAD (mm) | 42 ± 6 | 43 ± 5 | 0.591 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 12.7 ± 1.5 | 12.9 ± 1.7 | 0.201 |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73m2 ) | 56.4 ± 22.3 | 47.7 ± 19.9 | < 0.01 |
| Log-BNP (pg/mL) | 2.0 ± 0.4 | 2.2 ± 0.4 | < 0.001 |
| Log-hs-CRP (mg/dL) | -1.3 ± 0.5 | -1.0 ± 0.4 | < 0.01 |
| CAVI | 9.4 ± 1.2 | 10.1 ± 1.1 | < 0.001 |
| RAS inhibitor, n (%) | 239 (65) | 30 (52) | < 0.01 |
| β-blocker, n (%) | 72 (19) | 2 (3) | < 0.01 |
| Diuretics, n (%) | 75 (20) | 12 (21) | 0.692 |
| Statin, n (%) | 104 (28) | 15 (26) | 0.723 |
| HR | 95% CI | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; CAVI: cardio-ankle vascular index; RAS: renin- angiotensin system; eGFR: estimated glomerular filtration rate; hs-CRP: high sensitivity C reactive protein. | |||
| Age (≥ 75years) | 2.78 | 1.53 - 5.10 | < 0.01 |
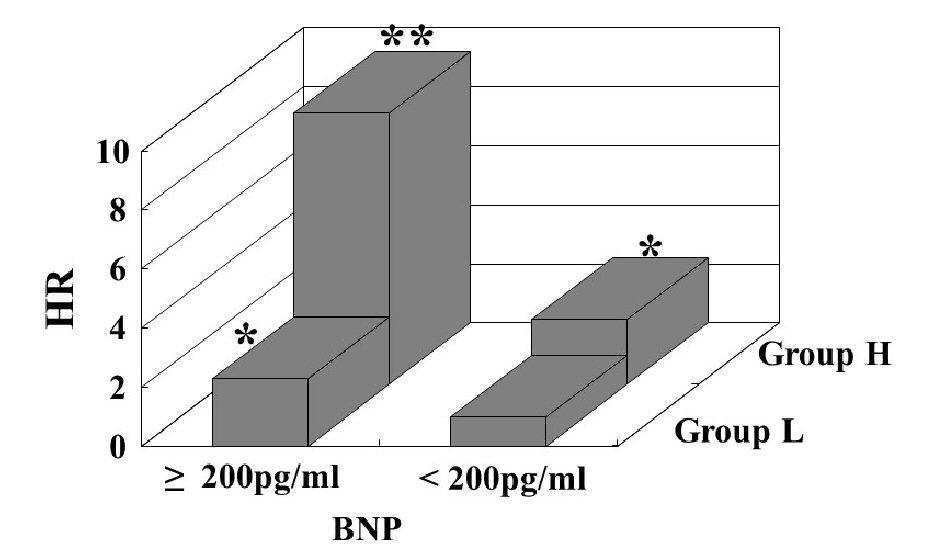
| Group H | 2.35 | 1.37 - 4.43 | < 0.01 |
| BNP (≥ 200pg/mL) | 2.22 | 1.21 - 3.52 | < 0.01 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 1.94 | 1.06 - 3.38 | < 0.05 |
| CAVI (≥ 10) | 1.82 | 1.07 - 3.19 | < 0.05 |
| β-blocker | 0.52 | 0.33 - 0.98 | < 0.05 |
| RAS inhibitor | 0.44 | 0.27 - 1.11 | 0.089 |
| eGFR (< 60mL/min/1.73m2) | 1.53 | 0.85 - 2.77 | 0.159 |
| hs-CRP (≥ 0.1mg/dL) | 1.41 | 0.79 - 2.53 | 0.190 |
| Current smoker | 1.31 | 0.84 - 1.73 | 0.204 |